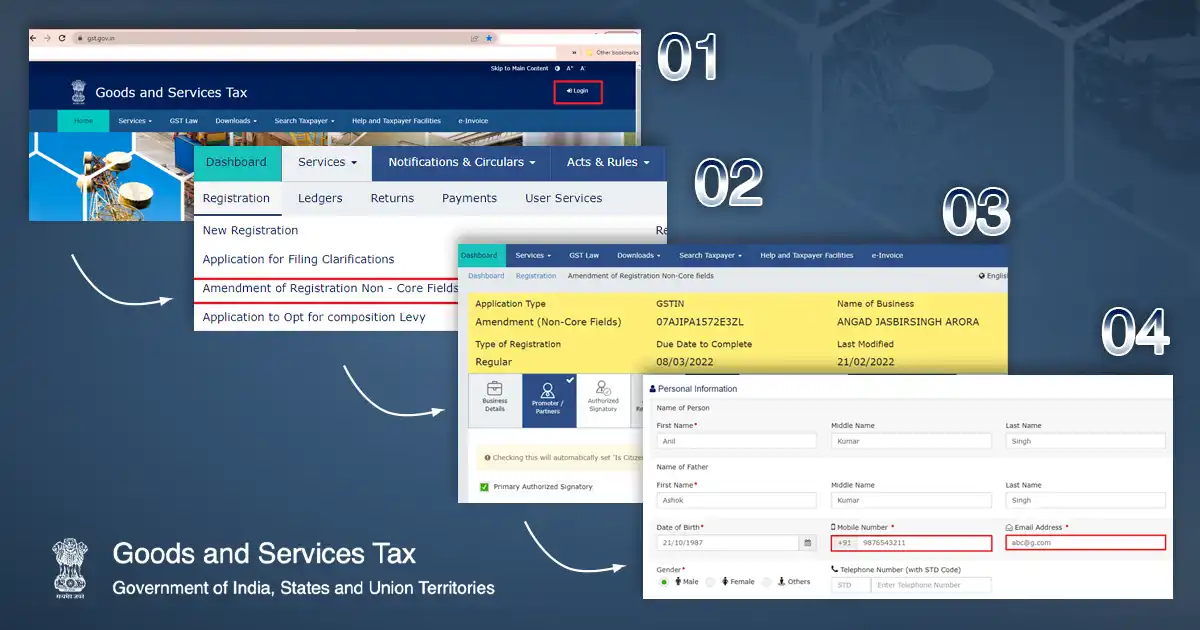
Businesses and individuals can complete the entire procedure through the official GST portal in the following manner:
Step 1: Generating Your Temporary Reference Number (TRN)
The first stage of GST registration involves generating a Temporary Reference Number (TRN), which acts as a temporary identifier for your application.
- Access the GST Portal: Begin by navigating to the official GST website: gst.gov.in.
- Initiate New Registration: On the homepage, click on the "Services" tab, then select "Registration," and finally choose the "New Registration" option.
- Fill Basic Details (Part A): On the registration page, select "Taxpayer", choose your State and District, enter your business name and PAN. Then add a valid email and mobile number, complete the Captcha, and click "PROCEED".
- OTP Verification and TRN Generation: You will receive separate One-Time Passwords (OTPs) on the provided mobile number and email address. Enter these OTPs for verification. Upon successful validation, a Temporary Reference Number (TRN) will be generated and displayed on your screen.
Step 2: Log in with TRN
Go to the GST portal, choose "New Registration" > "TRN", and log in using the OTP sent to your registered email and mobile.
Step 3: Access Saved Application
Click on "My Saved Application" and use the edit option to continue filling out Form GST REG-01.
Step 4: Fill in Business Details
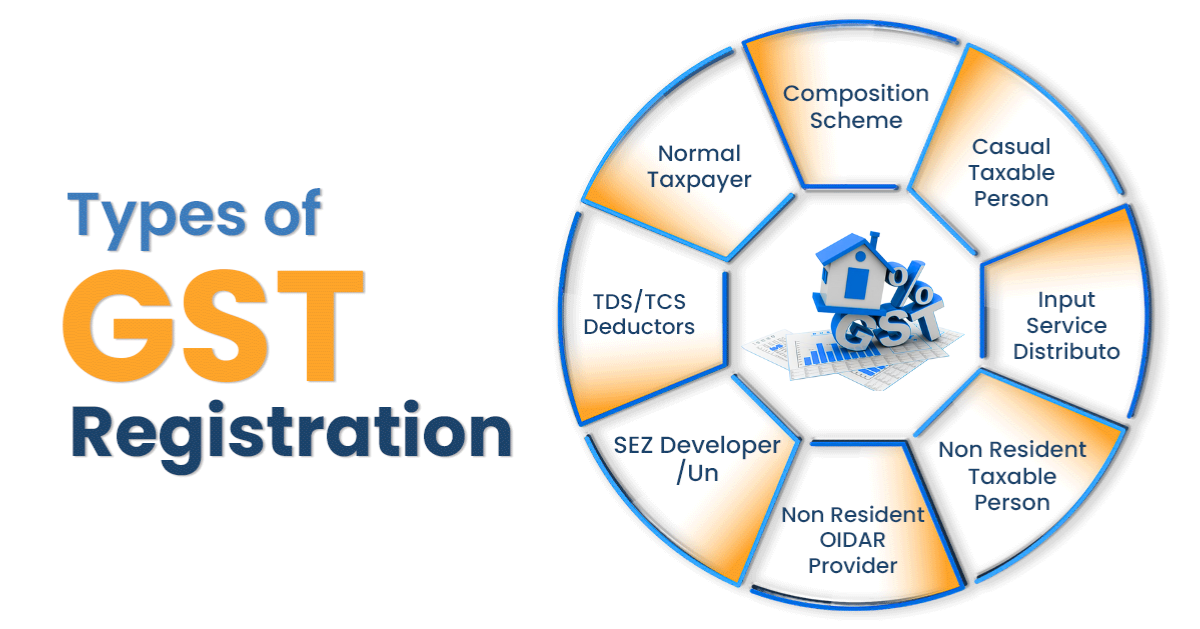
Enter your trade name, business type, district, codes, and dates for business start and GST liability. Choose the Composition Scheme if eligible.
Step 5: Promoter/Partner Info
Add details of promoters/partners like name, PAN, Aadhaar, contact, and DIN (if applicable).
Step 6: Authorized Signatory
Provide details and documents for the person handling GST compliance on behalf of your business.
Step 7: Business Address
Enter your main business address, upload proof, and mention any additional business locations.
Step 8: Goods & Services
List the goods/services you deal in with their HSN/SAC codes.
Step 9: Bank Details
Submit your bank account number, IFSC, and upload a cancelled cheque or statement.
Step 10: State-Specific Info
Add any additional information required by your state, if applicable.
Step 11: Aadhaar Authentication
Choose to verify via Aadhaar for faster processing, or skip and undergo manual verification.
Step 12: Final Submission
Review all details, tick the declaration, and submit using DSC, e-Sign, or EVC as per your business type. Once you successfully submit your GST registration application, you’ll receive an Application Reference Number (ARN) as confirmation.
This unique 15-digit number is crucial for tracking the status of your application online and will be sent to your registered email address and mobile number.