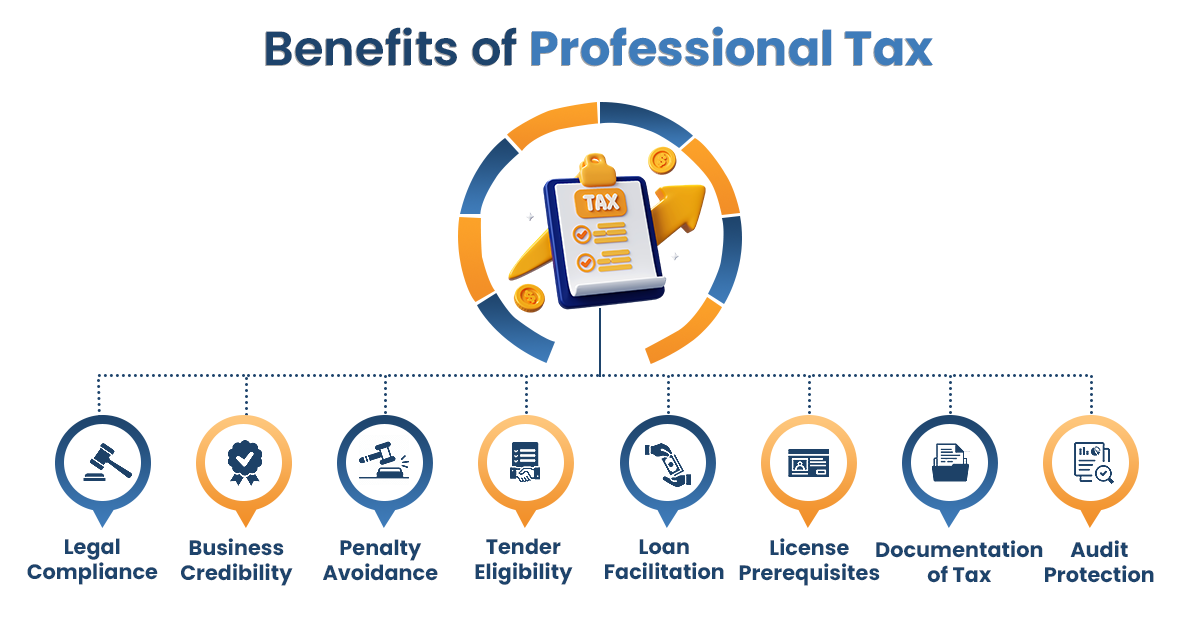
Professional tax registration is the process where employers and businesses register with their state's Commercial Tax Department for collecting and paying professional tax. It’s a state-level levy regulated by the State Professional Tax Acts, allowing governments to tax professions, trades, and employment.
According to Hindustan Times, Professional tax collections have increased by 27% in major Indian states over the last two years, with enforcement becoming significantly stricter. This trend demonstrates the growing importance of timely professional tax registration for businesses and professionals across India.
Types of Professional Tax Registration
Professional tax registration applies to various entities and situations. The two main certificates are PTEC and PTRC, but registration is also required in the following scenarios:
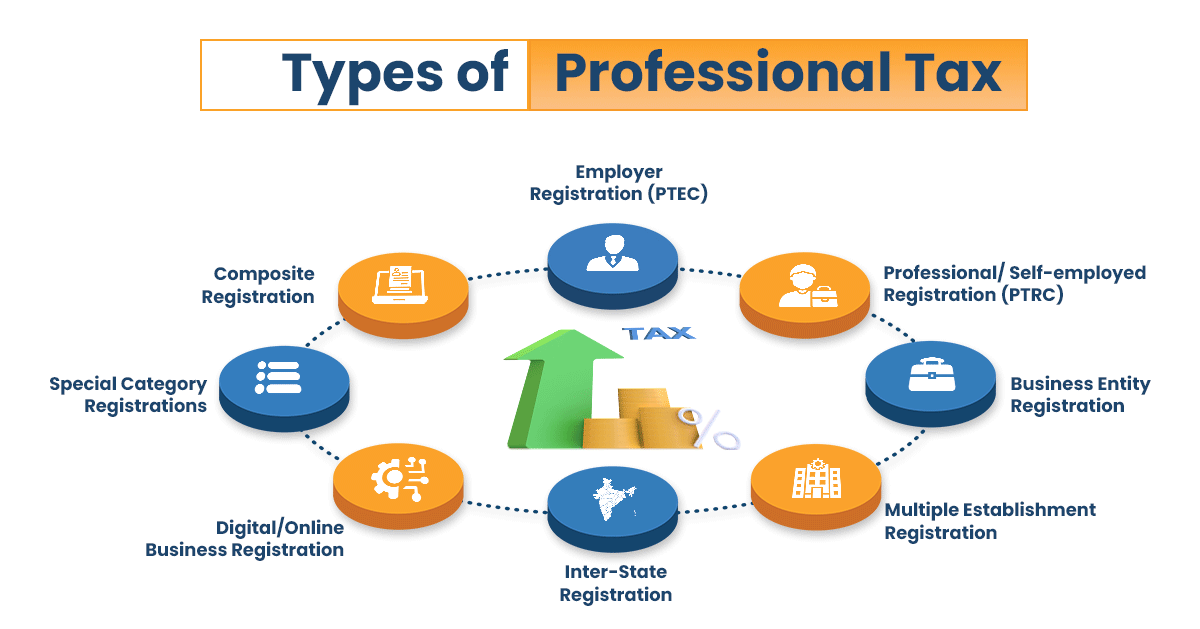
1. Employer Registration (PTRC - Professional Tax Registration Certificate)
Employers must obtain PTRC registration to deduct professional tax from employee salaries and remit it to the state. For instance, a software company with 50 employees in Karnataka needs this registration to deduct professional tax from its employees' salaries.
2. Professional/Self-employed Registration (PTEC - Professional Tax Enrollment Certificate)
This is mandatory for self-employed professionals, consultants, and individuals engaged in any trade or profession, for their professional tax liability. For example, a chartered accountant in Maharashtra must obtain PTEC registration for their professional tax compliance.
3. Business Entity Registration
Partnerships, LLPs, and other business entities must register for requirements based on their structure and state laws.
For example: a retail partnership in Tamil Nadu must register for professional tax according to its annual turnover.
a. Multiple Establishment Registration
Businesses with multiple locations in the same state must register each establishment separately.
For instance: a restaurant chain with 5 outlets in West Bengal needs individual professional tax registrations for each location.
b. Inter-State Professional Tax Registration
Businesses operating in multiple states must register in each one.
Example: A consulting firm serving Gujarat and Maharashtra needs separate registrations in both states.
c. Digital Platforms and Online Businesses Registration
Digital businesses and online service providers must meet state-specific registration requirements.
For instance: an e-commerce business in Telangana must register for professional tax, regardless of whether it has a physical retail location.
d. Special Category Registrations
Certain professions, such as doctors, lawyers, and architects, require specialized registration.
For example: lawyers in Kerala must register under a specific category for legal professionals.
e. Composite Registration
Combined registration options for professionals with multiple business structures in certain states.
For example: a doctor in Odisha with a private practice and a consultancy may qualify for combined registration.
Rules and Regulations for Professional Tax Registration
Professional tax registration is governed by state-specific regulations that outline the procedure for professional tax registration, eligibility, and compliance requirements.
1. Article 276 of the Constitution of India - Empowers states to levy taxes on professions, trades, callings, and employments, with a maximum professional tax limit of Rs. 2,500 per person annually.
2. State-specific Professional Tax Acts - Each state has its legislation (e.g., Maharashtra State Tax on Professions, Trades, Callings and Employments Act, 1975; Karnataka Tax on Professions, Trades, Callings and Employments Act, 1976).
3. Professional Tax Rules - Procedural regulations detailing registration, payment schedules, returns filing, and penalties in each state.
4. State Finance Acts - Annual modifications to professional tax slabs, exemptions, and procedural requirements for professional tax registration.
5. Municipal Corporation Acts - In some states, municipal bodies are authorized to collect professional tax within their jurisdiction.