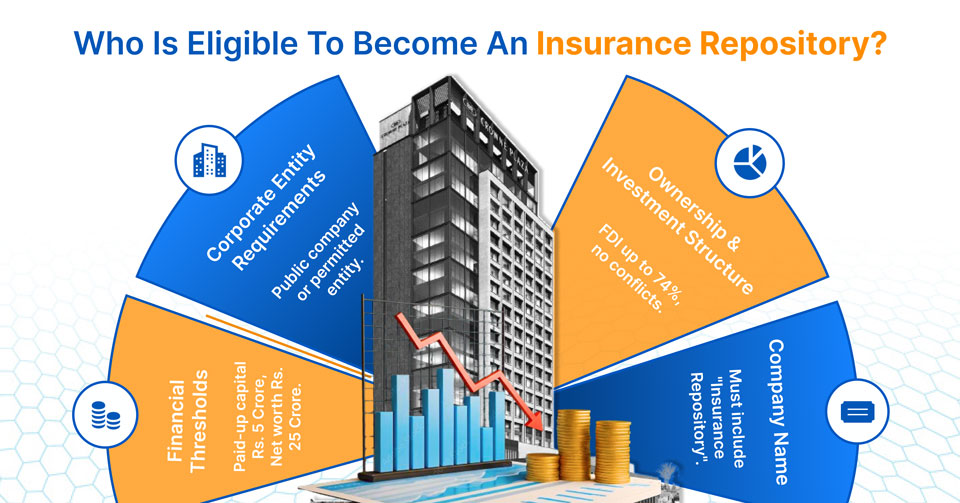
Any entity intending to maintain insurance policies in electronic format must obtain prior approval and registration as an Insurance Repository from the IRDAI (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India). This mandate ensures the secure, standardized, and regulated management of electronic insurance policies, which enhances transparency and access for policyholders.
At RegisterKaro, we simplify the rigorous insurance repository registration process, ensuring your entity smoothly navigates IRDAI's requirements to become a licensed insurance repository in India.
Objective of the Insurance Repository System
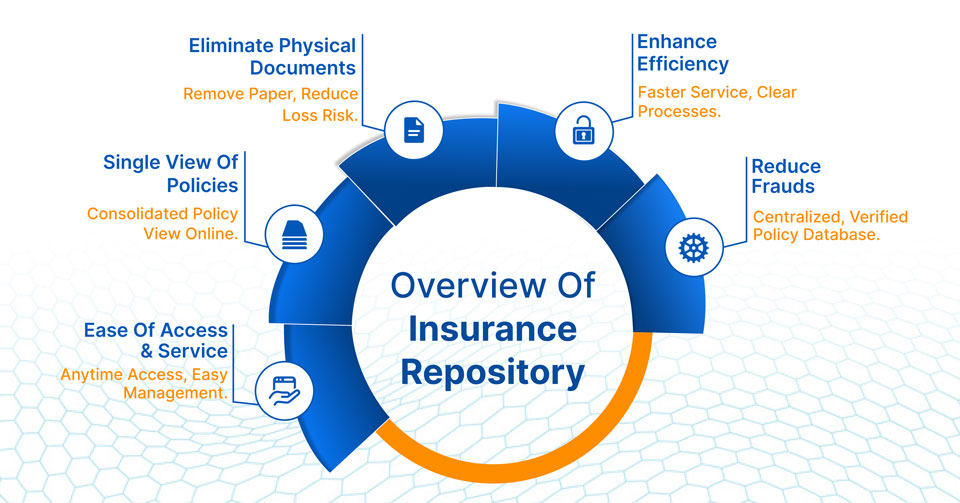
The IRDAI created the Insurance Repository System with one primary goal: to give policyholders a secure, central, electronic facility to hold all their insurance policies. This system aims to:
- Eliminate Physical Documents: Remove the need for physical paper insurance policy documents, reducing storage hassle and the risk of loss or damage.
- Single View of Policies: Offer policyholders a consolidated view of all their insurance policies from different insurers in a single Electronic Insurance Account (eIA). This helps policyholders track and manage their entire insurance portfolio effortlessly.
- Ease of Access and Service: Provide easy, anytime, anywhere access to policy details and facilitate quick changes, modifications, nominations, and premium payments.
- Enhance Efficiency and Transparency: Streamline policy servicing, reduce turnaround times for various requests, and bring greater transparency to the insurance ecosystem.
- Reduce Frauds: Minimize instances of fraudulent claims or misrepresentation by maintaining a centralized, verified database of policies.
- Boost Financial Inclusion: Encourage more people to buy insurance by simplifying the ownership and management process.
Entities like Central Insurance Repository Limited, National Insurance Repository, Karvy Insurance Repository Limited, and CDSL Insurance Repository Limited are key players in this system, ensuring that policyholders have multiple options to choose from for managing their e-insurance accounts securely and efficiently.