A trust is a legal arrangement where one person transfers property (the "settlor") to another person to hold and manage (the "trustee") for the benefit of a third person or group (the "beneficiary") or a specific purpose.
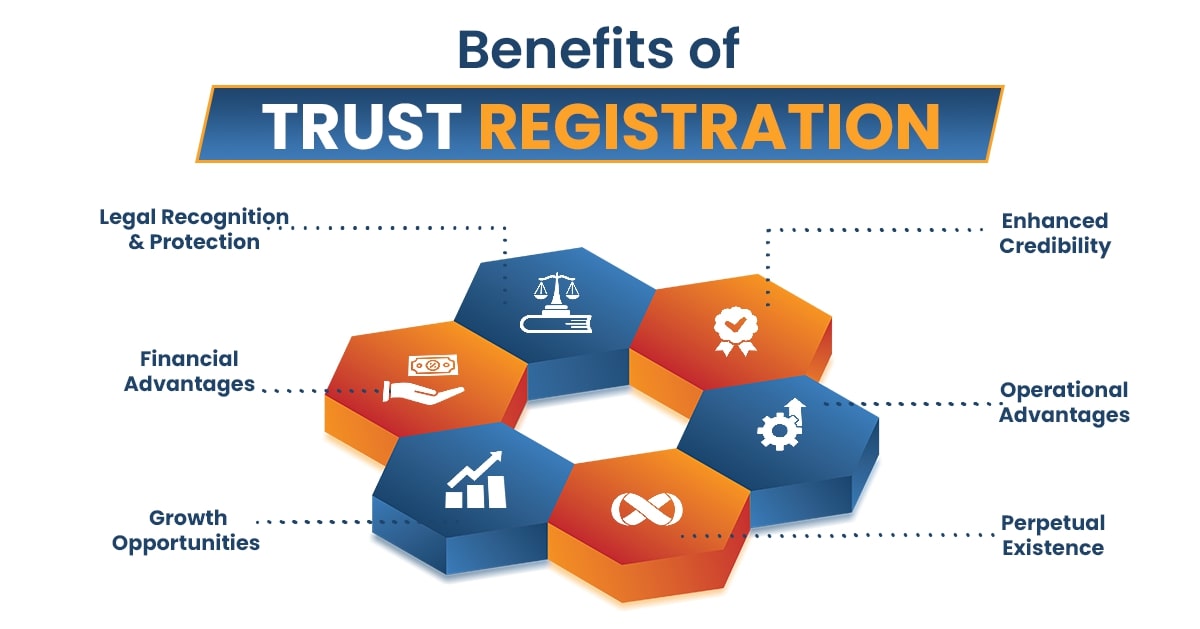
Trust Registration is the formal process of legally establishing a trust under various trust registration acts. This registration provides legal recognition, enables tax benefits, and ensures the trust operates as intended.
Types of Trusts Available for Registration in India

- Public Trusts: Established for public benefit purposes like education, healthcare, and poverty alleviation.
- Private Trusts: Created for specific beneficiaries, often family members.
- Religious Trusts: Focused on religious activities and the maintenance of places of worship.
- Charitable Trusts: Dedicated to charitable causes like relief for the poor, education, and medical relief.
Objectives of a Trust
The main objective of Trust Registration in India is to give legal validity and operational structure to the intentions of the settlor. It helps in:
- Legally binding the trustees to the trust's objectives.
- Protecting the assets held within the trust.
- Ensuring the benefits reach the intended beneficiaries.
- Enabling the trust to receive donations and exemptions during ITR filing.
- Providing a framework for the administration and management of the trust.
- Allowing the trust to sue or be sued in its capacity.
- Facilitating GST registration for the trust if it undertakes taxable activities.
For settlers and beneficiaries, registration ensures the trust’s objectives are legally enforceable.
Laws Governing Trust Registration in India
To register your trust, you must understand the laws that define its formation and operation. These statutes and authorities ensure your trust gains legal validity and access to benefits.
Legal Framework
Trust registration in India is primarily governed by:
- The Indian Trusts Act, 1882 - Provides the foundational legal framework for private trusts.
- The Bombay Public Trusts Act, 1950 (applicable in Maharashtra and Gujarat).
- State-specific Trust Acts in various states for public trusts.
- The Registration Act, 1908 - Governing the registration of trust deeds.
- The Income Tax Act, 1961 - For tax implications and exemptions.
Regulatory Authorities for Trust Registration in India
To maintain legal validity and access government benefits, trusts must interact with the following authorities:
- Registrar/Sub-Registrar Office (under the Registration Act, 1908): Responsible for registering the trust deed, confirming the trust’s legal existence.
- Charity Commissioner (in applicable states): Oversees registration, financial audits, and handles complaints for public charitable trusts.
- Income Tax Department: Grants the 12A and 80G registration, which are necessary for tax exemptions and donor benefits.