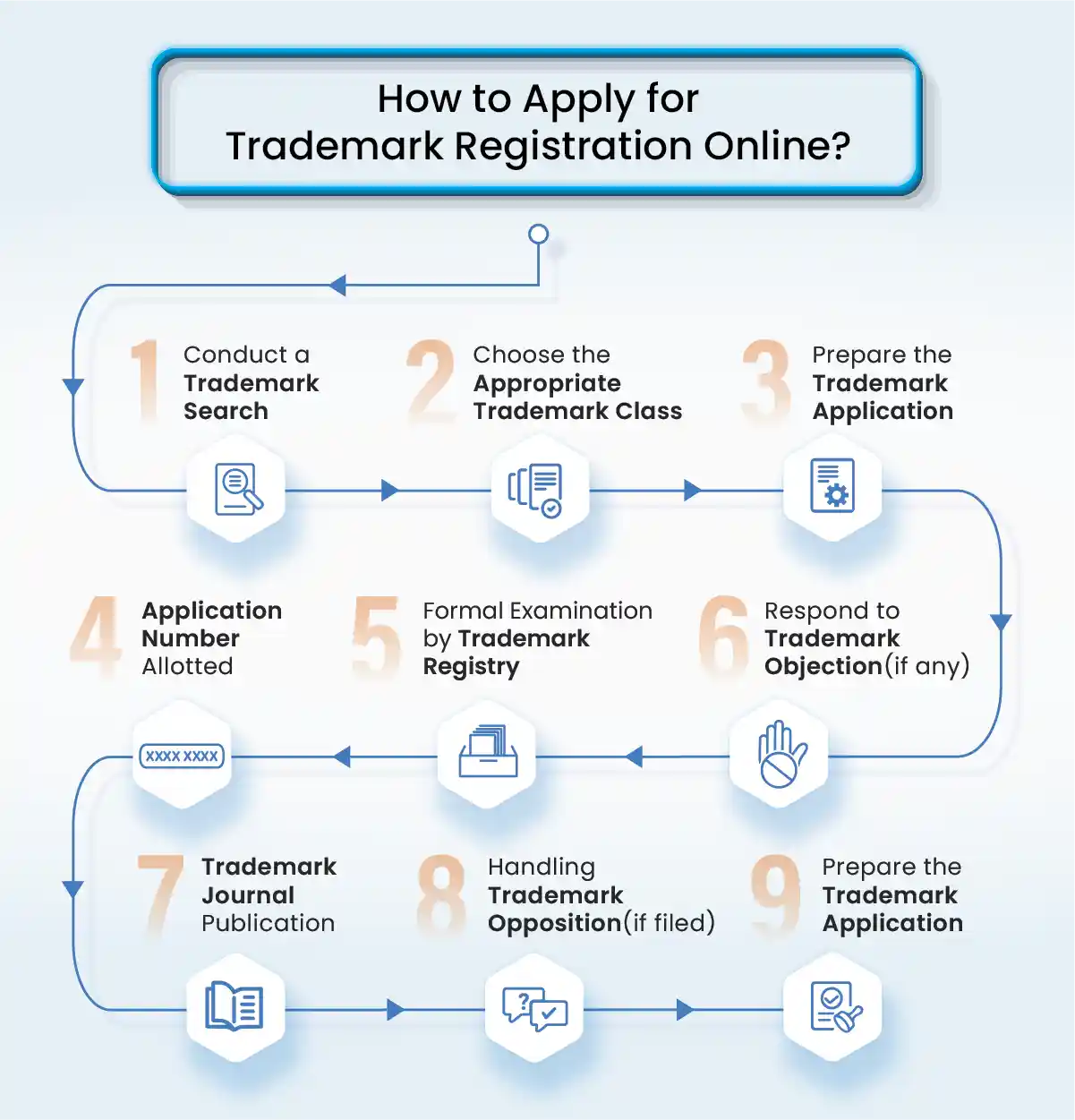
Trademark registration in India is governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999. It allows individuals and businesses to legally protect their brand names, logos, and unique identifiers used for goods or services. Once registered, the trademark owner gets exclusive rights to use the mark across India and can take legal action against infringement.
Trademark registration is often referred to as brand registration, brand name registration, or logo registration, depending on what is being protected. It not only helps you safeguard your business or product name but also protects your logo, tagline, and other visual elements.
This ensures that no one else can use your brand identity without permission, giving you exclusive rights over your intellectual property.
According to the World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO), India has over 3.2 million active trademarks, making the nation the 2nd largest holder of active trademarks. This sharp rise shows that more and more businesses in India are recognizing the importance of protecting their brand identity in today’s competitive and expanding economy.
What is a Trademark?
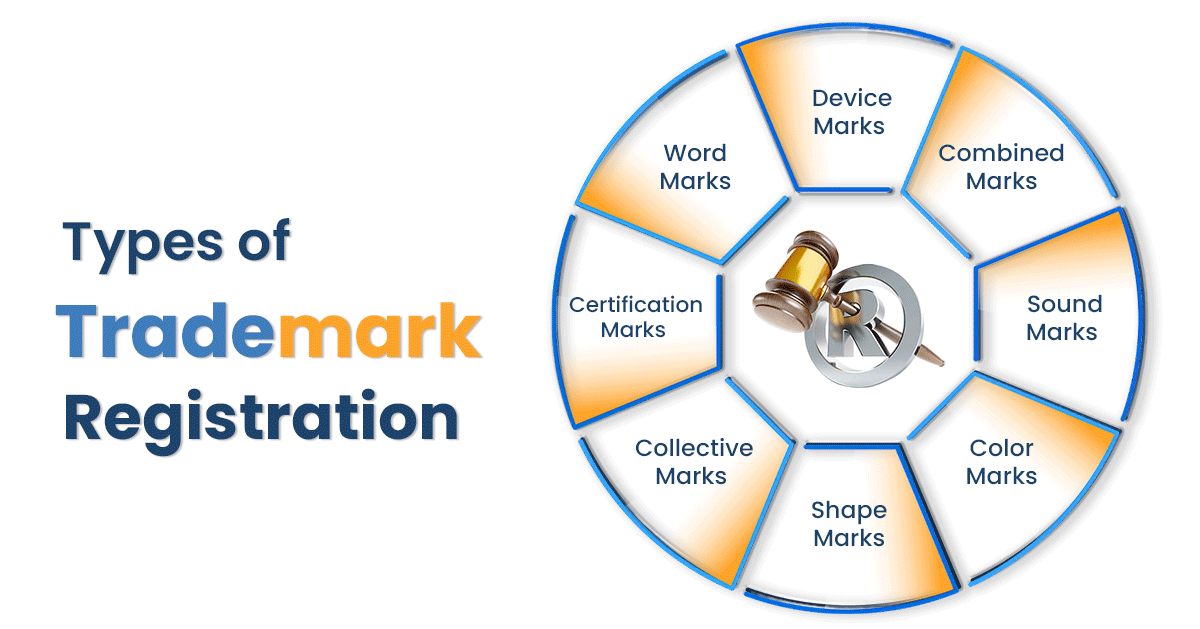
A trademark is a unique sign, word, symbol, logo, design, sound, or color combination that distinguishes one business’s goods or services from others. It helps consumers identify the source of products or services and builds brand trust over time.
Examples of trademarks include:
- Brand names
- Business names
- Logos and symbols
- Slogans and taglines
- Sounds or jingles
- Product packaging shapes