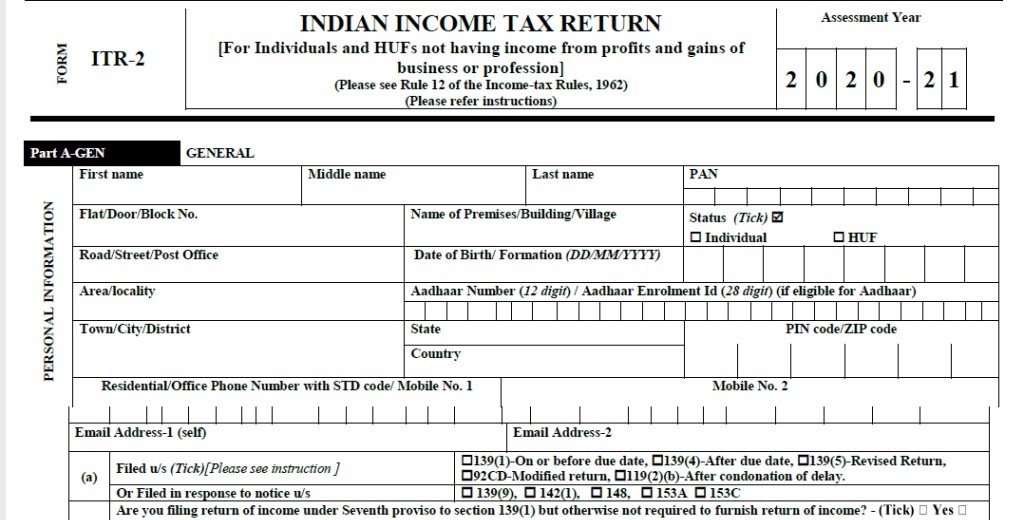
The process of filing Form ITR 2 is designed to be user-friendly on the income tax e-filing portal.
1. Prerequisites Before You Start Filing
Before initiating the filing process, ensure the following documents and data are readily available:
- Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Aadhaar number
- Bank account details, including IFSC code
- Form 16 issued by your employer
- Form 26AS, Annual Information Statement (AIS), and Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS)
- Capital gains computation statements for listed securities, mutual funds, and property
- Details of house properties, including rental income, municipal taxes, and interest on home loans
- Information related to foreign income or assets (if applicable)
- Records of income from VDAs, such as cryptocurrencies or NFTs
- Details of any advance tax or self-assessment tax paid
2. Logging into the Income Tax Portal and Selecting the ITR-2 Form
Visit the official Income Tax e-filing portal at incometax.gov.in. Log in using your PAN, password, and captcha, or use Aadhaar OTP or net banking for secure access.
The portal now automatically pre-fills data like Form 26AS, AIS, TIS, etc., in the ITR-2 form to simplify your filing process.
Once logged in:
- Go to e-File > Income Tax Returns > File Income Tax Return
- Select the appropriate Assessment Year
- Choose ‘Online’ as the filing mode
- Select the user type: Individual or HUF
- From the list of ITR forms, select ITR-2
Now you can easily download the ITR 2 form PDF from the portal.
3. Navigating the Pre-filled Data: Verification and Editing
The portal auto-populates data from your Form 26AS, AIS, and TIS. This includes:
- TDS deducted by employers and other deductors
- Bank interest income
- Dividend income
- Capital gains from listed securities
Each field must be thoroughly verified. If discrepancies exist, corrections should be manually made to ensure data integrity.
4. Filling Your Income Details: Salary, House Property, and Other Sources
Enter income details in the relevant schedules:
- Schedule S: Provide salary and pension details, based on Form 16
- Schedule HP: Report rental income, self-occupied property, interest paid on housing loans, and municipal taxes
- Schedule OS: Disclose income from dividends, savings interest, fixed deposits, lotteries, or VDAs
Ensure that all deductions under Chapter VI-A (Sections 80C to 80U) are correctly claimed.
5. Reporting Capital Gains Accurately
Use Schedule CG to report all capital gains:
- Provide ISIN, scrip name, acquisition and sale dates, and sale consideration
- Use the indexed cost of acquisition where eligible
- Enter exemptions claimed under Section 54, 54EC, 54F, etc.
- If multiple transactions exist, you may upload a CSV template provided by the portal for bulk entry
Maintain accuracy, as errors in capital gains computation can lead to notices or defective returns.
6. Completing the Filing: Tax Payment and Submission
After all income schedules are filled:
- The system computes the total tax liability or the refund amount
- If additional tax is due, pay via Challan 280 under self-assessment tax
- Review all schedules thoroughly and ensure data consistency
- Click ‘Proceed to Preview’ to generate a summary
- On confirmation, click ‘Submit’ to file the return
7. E-Verify Your ITR-2 Return
Post-submission, e-verification is compulsory for return validation. Choose from:
Note: E-verification must be completed within 30 days of filing the return. If not verified within this period, your ITR will be treated as invalid.