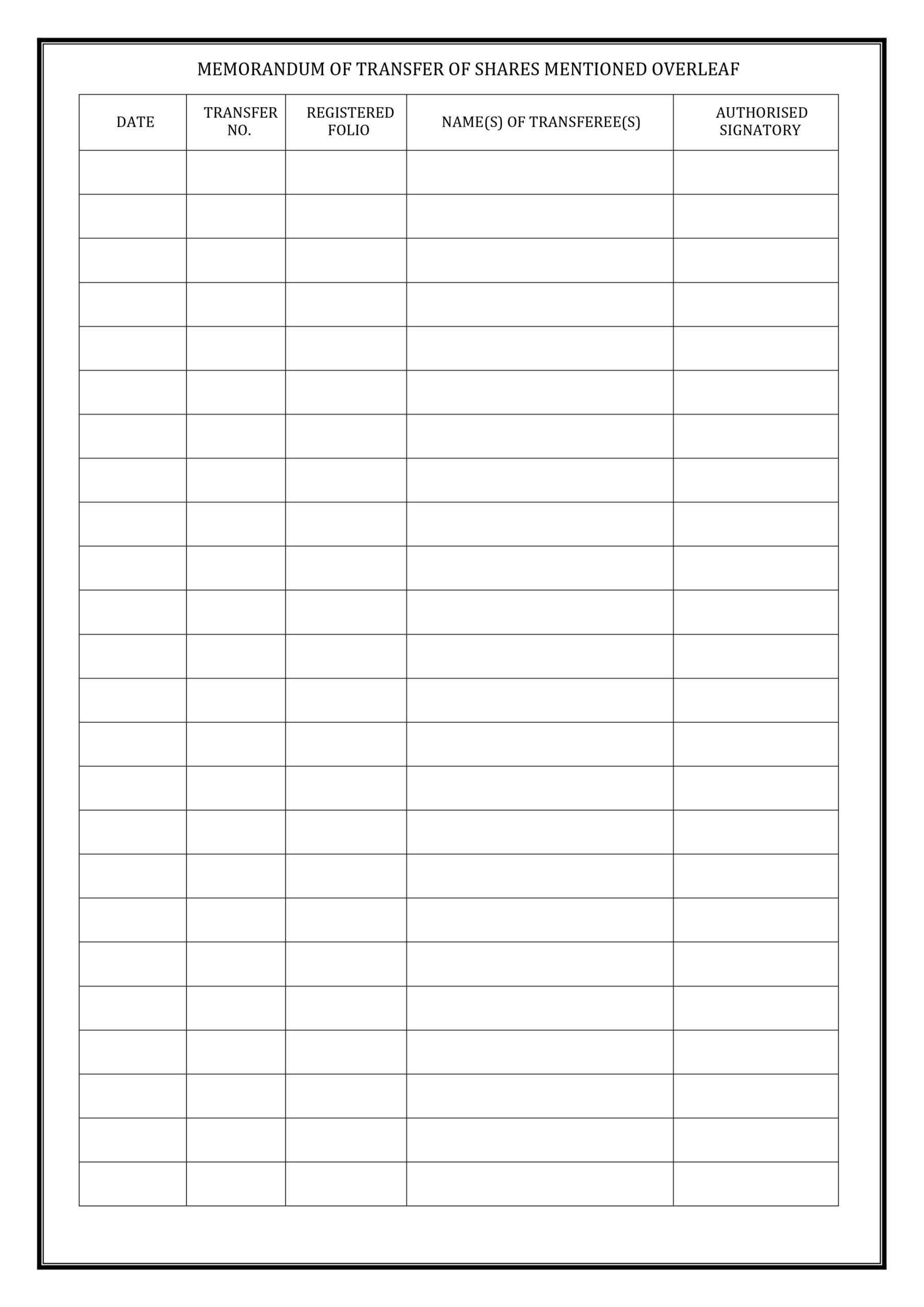
The issue of shares is the process through which a company raises capital by offering ownership units called shares to investors. These shares represent a claim on the company’s assets and earnings. When a company issues shares, it essentially sells a portion of itself to raise funds for business activities like expansion, product development, or debt repayment.
Companies can issue shares to the public (in a public offering) or privately to specific investors. There are different types of share issues—such as equity shares, preference shares, and rights issues—depending on the company's needs and the structure of the offer. Each type comes with its own set of rights, responsibilities, and financial implications for both the issuer and the shareholder.
Why Do Companies Issue Shares?
Companies primarily issue shares for several key reasons:
- Raising Capital: This is the most common reason. Funds raised can fuel expansion, acquire assets, invest in research and development, pay off debt, or simply boost working capital.
- Funding Growth: Equity financing provides the significant funds a company might need to scale operations, enter new markets, or launch new products.
- Improving Financial Standing: Issuing shares can improve a company's debt-to-equity ratio, making it more attractive to lenders.
- Rewarding Employees: Companies might issue shares to employees as part of incentive plans (like Employee Stock Ownership or ESOPs) to boost motivation and loyalty.
- Acquisitions: Shares can be used as currency to acquire other businesses.