The process of filing ITR-7 is completely digital and must be done through the e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
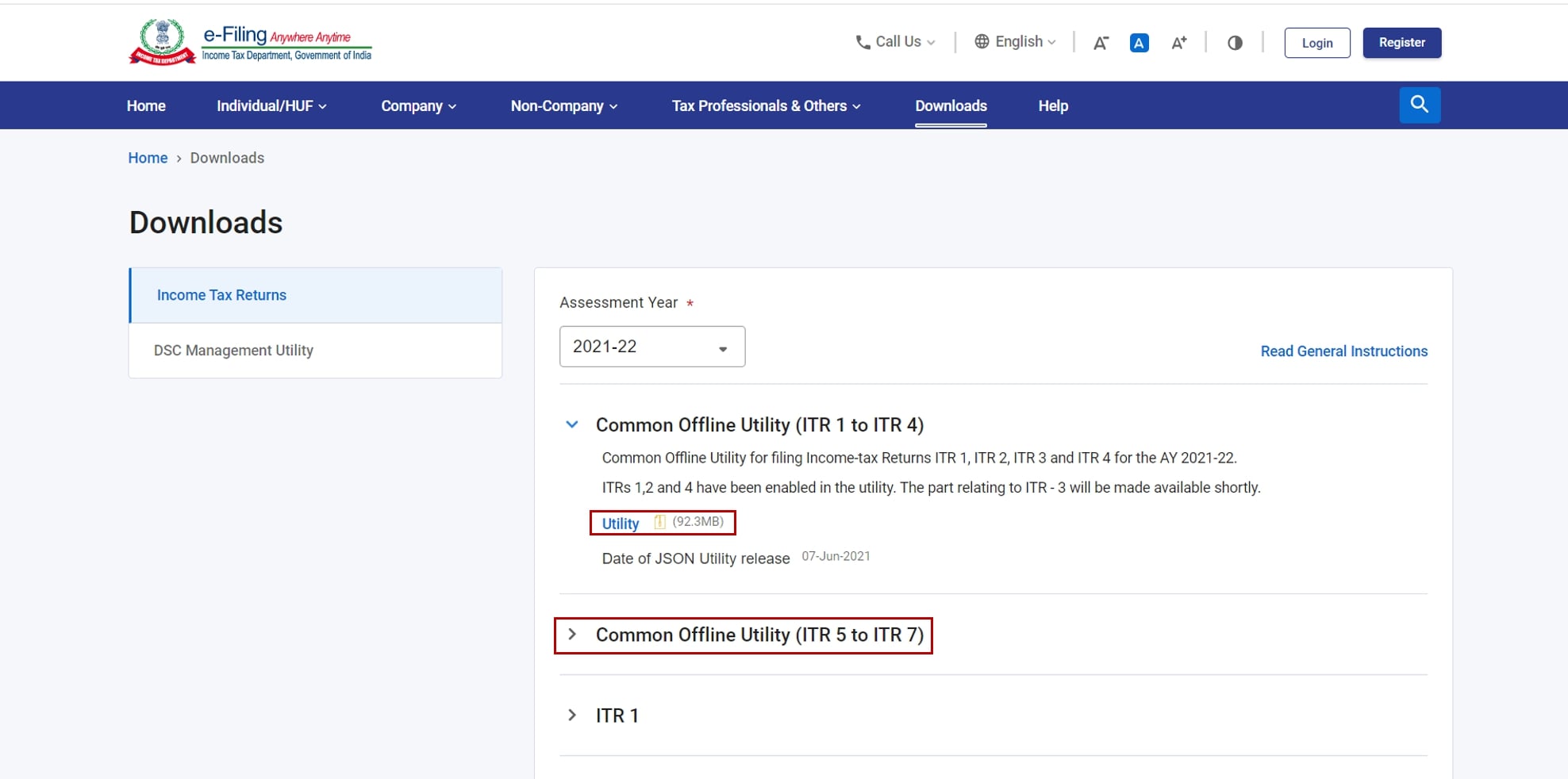
Step 1: Download the Utility
First, you need to go to the official e-filing portal (incometax.gov.in) and download the latest ITR-7 utility. This utility is an offline tool that helps you prepare your return. It's available in either Java or Excel-based ZIP format.
Step 2: Prepare the Return
Open the utility and enter all required data, such as:
- PAN and Aadhaar number
- Registration details under the Income Tax Act sections
- Income and exemption details
- Financial statements, donor list, and asset/liability info
Select applicable schedules like EI, VC (Voluntary Contributions), and others. Ensure accurate and consistent entries with supporting documents.
Step 3: Validate the Return
The utility has a 'Validate' button that checks for any common errors or inconsistencies in the data you've entered. You must validate each section to ensure the information is correct and complete.
Step 4: Generate JSON File
Once all the sections are validated, you can generate a JSON file. This file contains all the data you've entered in a format that can be uploaded to the e-filing portal.
Step 5: Upload the Return
Log in to the e-filing portal, then:
- Go to e-File → Income Tax Return → Upload Return
- Select ITR-7, AY 2025–26, and upload the JSON file
- Attach any required reports (like audit reports under Section 44AB or Section 10(23C))
Step 6: E-Verifying Your ITR-7
After filing ITR-7, it is mandatory to verify the return. You must e-Verify within 30 days of filing; otherwise, the return will be treated as invalid and incomplete. The accepted methods for verification include:
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): Mandatory for most trusts and political parties. Use a valid DSC registered on the e-filing portal.
- Aadhaar OTP: If the principal officer’s Aadhaar is linked with PAN, an OTP can be sent to their Aadhaar-linked mobile for quick verification.
- Electronic Verification Code (EVC): The EVC is a 10-digit alphanumeric code that can be generated using net banking, a bank account, a Demat account, or an ATM. It is valid for a limited time and must be used before the expiration date.
- Send ITR-V to CPC: If digital options fail, send a signed physical copy of ITR-V to Centralized Processing Centre (CPC) Bengaluru within 30 days. However, this method is being phased out and should be used only when no digital option is available.
Step 7: Acknowledgement (ITR-V)
After successful submission and e-verification, an acknowledgement (ITR-V) is generated. You can download this for your records. It serves as proof that your ITR-7 has been filed and verified.