Did you know that every registered company in India is legally mandated to have a unique Corporate Identification Number (CIN)? The CIN number is a 21-character alphanumeric code and acts as the backbone of corporate identification in India.
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), through the Registrar of Companies (RoC), issues the CIN to all companies registered under the Companies Act, 2013 (earlier Companies Act, 1956). It serves as a company’s legal identity and is used extensively for compliance, regulatory filings, and stakeholder verification.
Did You Know? CIN number is also known as the Company Registration Number in other countries. In this article, we’ll explore such interesting facts, components, relevance, and importance of a CIN for companies, along with practical tips on how to find, update, and use it correctly.
What is a CIN Number?
Issued by the RoC, the CIN number means the figures representing your company’s official identity card. It helps regulators, banks, investors, and other businesses identify your company quickly and verify its legal status. A CIN is used extensively for regulatory purposes, tax filings, and corporate communication.
Some key features of a CIN include:
- It uniquely identifies every registered company in India.
- Companies use the CIN in compliance tasks such as filing taxes, submitting legal documents, and completing MCA filings.
- The CIN reveals important details about a company, including:
- Listing status (listed or unlisted)
- Type of company (Private Ltd., Public Ltd., etc.)
- Industry code
- State of registration
- Year of incorporation
- RoC code
- Unique registration number
- Businesses must mention the CIN on official documents like invoices, letterheads, annual reports, and e-forms filed with the MCA.
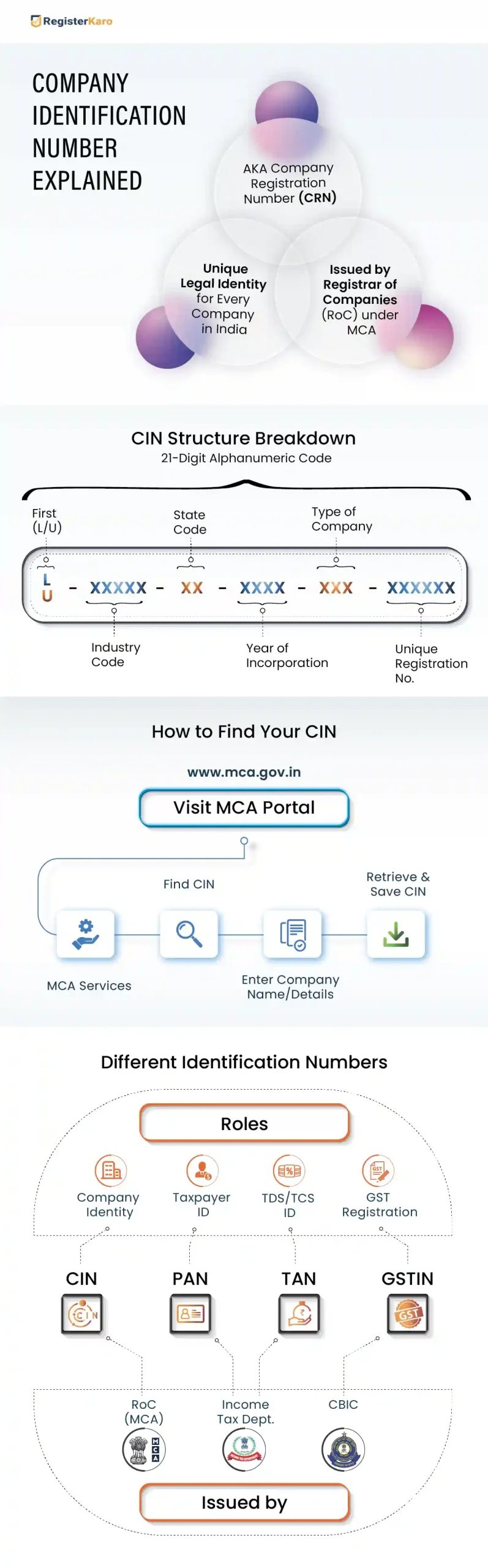
Structure of a CIN Number
A CIN follows a 21-character structure that reveals crucial information about the company. Each segment in a CIN number format has a specific meaning:
| Segment | Code Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Listing Status | L / U | Indicates whether the company is Listed (L) or Unlisted (U) |
| Industry Type | 72345 | Represents the company’s business sector or activity |
| State Code | KA | Two-letter code for the state of registration (e.g., KA for Karnataka, MH for Maharashtra) |
| Year of Incorporation | 2025 | Shows the year when the company was incorporated |
| Ownership Type | PLC | Specifies the type of company (e.g., PLC- Public Limited Company, PTC- Private Limited Company) |
| Registration Number | 123456 | A unique 6-digit number assigned by the RoC |
This structured format ensures that anyone, including regulators, banks, or business partners, can easily interpret the company’s identity and registration details at a glance.
Importance of a CIN Number of a Company
Having a CIN number for companies is not just a regulatory requirement; it serves as the official identity of every registered company in India. It ensures transparency, builds trust, and supports seamless compliance.
Let’s understand the criteria for getting a CIN number while registering a company:
- Legal Identification: CIN acts as the legal ID for every registered company in India. This enables clear recognition by government authorities and regulators.
- Mandatory for Compliance: CIN is required for filing tax returns, MCA filings, and other statutory obligations.
- Used in Official Documents: Businesses display their CIN on invoices, letterheads, annual reports, and all official communications.
- Easy Verification for Stakeholders: Investors, suppliers, and other stakeholders can quickly verify a company’s registration and compliance status with its CIN.
When a company omits its CIN on official documents, it faces penalties and compliance risks. By displaying the CIN consistently, businesses protect their reputation and avoid legal issues.
CIN Number Check: How to Find It?
You can quickly find a company’s CIN through the MCA portal. Here’s how to get a CIN number:
- Visit the MCA Website: Open the official MCA portal at mca.gov.in.
- Navigate to “Find CIN”: Go to the “MCA Services” section and click on “Find CIN.”
- Enter Company Details: Provide the company’s name, registration number, or previous CIN to search.
- Review the Results: The system will instantly display the company’s CIN, along with other registration details.
- Save the Information: Record the CIN for compliance filings and future reference.
The MCA portal provides accurate and up-to-date company details, making it the most reliable way to find a CIN.
CIN Number vs Other Identification Numbers
CIN plays a vital role in a company’s identification. However, businesses and individuals also rely on other identification numbers such as PAN, TAN, and GSTIN. Each serves a distinct purpose. The table below highlights their differences:
| Aspect | CIN | PAN | TAN | GSTIN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identifies registered companies | Identifies taxpayers for Income Tax | Identifies entities deducting or collecting tax at source | Enables GST-related transactions |
| Issuing Authority | RoC under MCA | Income Tax Department, issued via NSDL/UTIITSL | Income Tax Department via NSDL/UTIITSL | Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) |
| Applicability | Only to companies registered under the Companies Act | To individuals and all types of entities | To employers or entities required to deduct or collect tax at source | To businesses registered for GST |
CIN applies only to companies registered with the MCA. PAN and TAN cover a wider range of entities, while GSTIN applies only to GST-registered businesses.
Steps to Update or Rectify a Company Registration Number
Companies may need to update their CIN in specific situations, such as:
- Change in Company Address: Relocating to a different state.
- Change in Business Structure: Converting from private to public limited or vice versa.
To update or rectify the CIN, follow these steps:
- File Appropriate Forms:
- Companies must file Form INC-22 for address changes.
- Use relevant MCA forms for changes in ownership type or other updates.
- Attach Supporting Documents:
Provide proof, such as board resolutions, utility bills, or lease agreements, in case of address changes. - Pay Applicable Fees:
Complete the payment through the MCA portal as per the prescribed fee schedule. - Wait for Approval:
The RoC reviews the submission and approves the updated CIN after verification.
Keeping your CIN details updated ensures smooth compliance with the Companies Act, 2013, and avoids penalties for incorrect corporate records.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Getting a CIN Number
Here’s what you should keep in mind while applying for a CIN:
- Missing CIN on Official Documents: Always include the CIN on all invoices, letterheads, and contracts. The Companies Act, 2013, makes it mandatory, and missing it can attract penalties.
- Confusing CIN with PAN or GSTIN: Treat each identification number separately. CIN applies only to companies registered with the MCA, while PAN, TAN, and GSTIN serve different tax and compliance purposes.
- Using an Outdated CIN After Change: Update the CIN immediately after a company changes its registered office (to another state) or converts from private to public. Using an old CIN creates compliance issues.
- Entering Incorrect Details During MCA Filing: Double-check the CIN when filing forms on the MCA portal. Even a single wrong character can lead to rejected submissions or delayed approvals.
- Not Keeping CIN Accessible: Many businesses fail to keep their CIN handy for quick reference. Store it securely and share it with key stakeholders to avoid delays in compliance or legal matters.
- Ignoring Verification of CIN in Public Records: Regularly verify the CIN on the MCA portal to ensure the company’s details remain accurate and updated. This step helps avoid discrepancies in government records.
Conclusion
A company proves its trust and credibility by following government rules, and the CIN is a key part of this process. The CIN gives every company a unique identity, makes compliance easier, improves transparency, and helps in smooth dealings with authorities, investors, and other stakeholders.
You should always check your company’s CIN details on the MCA portal and update them if there is any change, such as a new office address or a change in company type. Keeping your CIN correct and updated helps you avoid penalties and builds confidence among stakeholders.
Take Action Now: Visit the MCA portal or consult a professional to ensure your company’s CIN and other compliance requirements are properly managed!
Frequently Asked Questions
A Corporate Identification Number (CIN) is a unique 21-digit alphanumeric code assigned by the Registrar of Companies (RoC). It serves as the official identity of a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013.