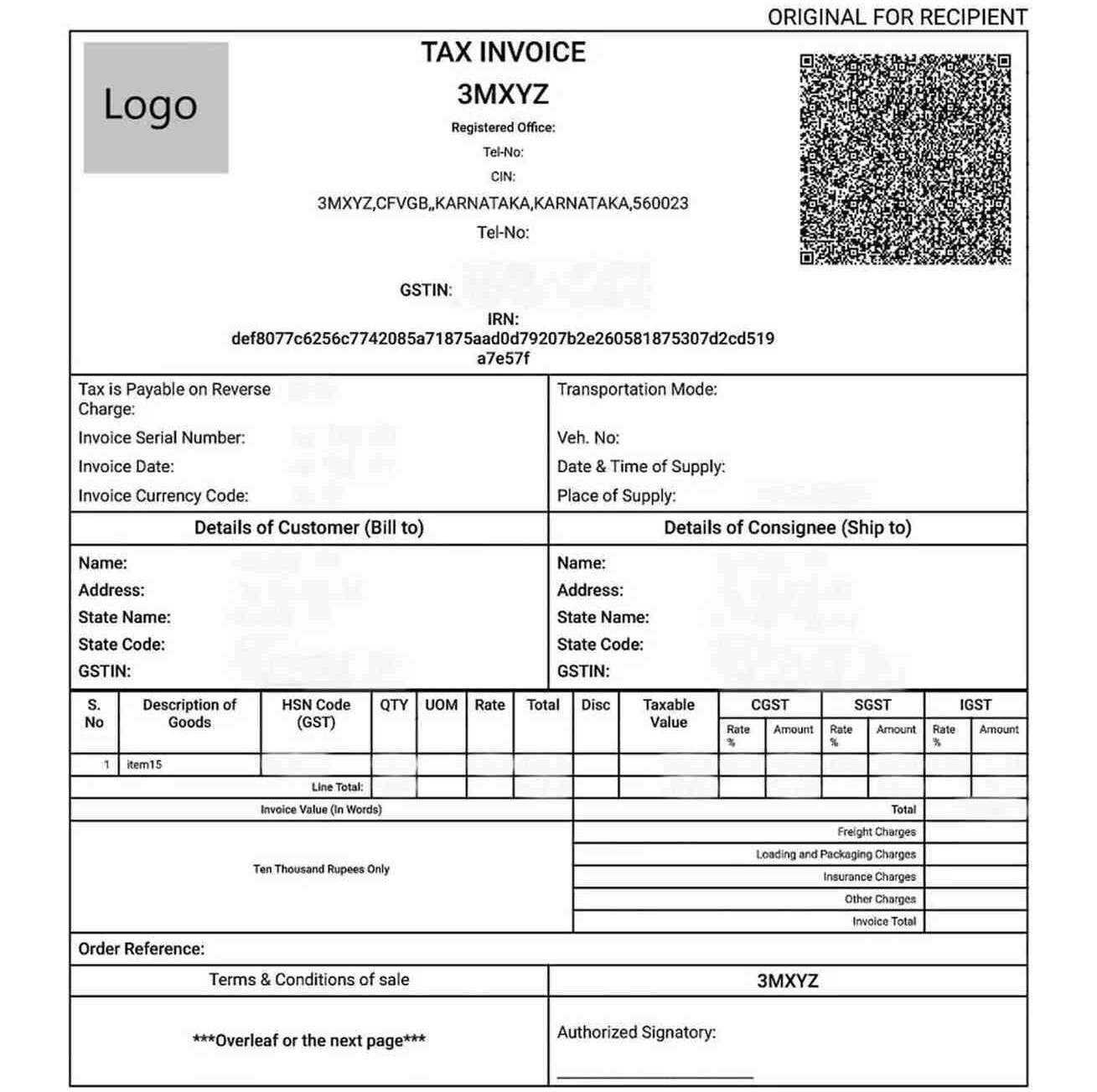
GST E-Invoice does not mean creating invoices on the GST portal. Instead, it's about reporting already generated invoices to a government-designated portal, the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), for validation and registration. When you generate an invoice in your accounting or billing software, the details are sent to the IRP.
You can keep generating invoices through your existing billing or ERP system without any major changes to your workflow. The only extra step is to send the invoice details in a prescribed JSON format to the IRP for authentication.
The IRP checks the data, creates a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN), digitally signs the invoice, and attaches a QR code to it. Once the IRP verifies and signs the invoice, it becomes a valid GST e-invoice. This process ensures standardized data and facilitates real-time B2B reporting to the GST system.
Why Was E-Invoicing Introduced Under GST in India?
The shift to e-invoicing under GST was driven by several key goals:
- Curb Tax Evasion: By ensuring real-time reporting of invoices, it becomes much harder for businesses to create fake invoices or manipulate sales figures, thus reducing tax evasion.
- Automate Compliance: It automates the process of filing GST returns, especially GSTR-1, as the data from GST E-Invoice is directly populated, reducing manual errors and saving time.
- Improve ITC Matching: With real-time invoice data, the system can more accurately match Input Tax Credit (ITC) between buyers and sellers, minimizing disputes and discrepancies.
- Standardize Data: It brings uniformity to invoice data across different businesses and software, making data analysis and reconciliation much easier for both taxpayers and tax authorities.
- Eliminate Fake Invoices: The unique IRN and digital signature make it almost impossible to generate or use fake invoices.
- Facilitates Faster GST Refunds: With accurate, real-time reporting, e-invoicing speeds up the verification process, leading to quicker GST refunds.
Key E-Invoice Words You Must Know
To navigate the GST E-Invoice portal and process, knowing these terms is essential:
-
IRP (Invoice Registration Portal)
This is the central government portal where taxpayers upload their invoice details for validation. It's the gateway for generating your GST E-Invoice. Currently, there are multiple IRPs operated by the NIC (National Informatics Centre) and other government-approved private entities.
-
IRN (Invoice Reference Number)
This is a unique 64-character hash generated by the IRP for each valid invoice. It's based on the supplier's GSTIN, invoice number, financial year, and document type, ensuring its uniqueness. No two invoices can have the same IRN.
-
QR Code
A Quick Response Code is a machine-readable barcode generated by the IRP and embedded in the GST E-Invoice. It contains key invoice details like GSTIN of the supplier and the recipient, IRN, invoice value, and date, allowing for quick verification by tax officers and buyers.
-
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
This is the standardized digital format in which invoice data must be prepared and uploaded to the IRP. It ensures uniformity and ease of data exchange between different systems.