
Annual Information Statement: An Overview
Launched by the income tax department, the Annual Information Statement (AIS) consolidates your entire year’s financial activities into one clear report. Running a business in India means juggling many financial responsibilities, yet few tools rival the power of AIS. A unified view helps you spot discrepancies early, stay compliant, and tune your tax strategy.
This blog breaks down everything you need to know about the annual information statement, from accessing to using it for business decisions.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or a new business owner, mastering your AIS is essential for financial transparency and tax compliance.
What is an Annual Information Statement?
Think of the AIS as your PAN’s money log, listing every transaction. Issued by the Income Tax Department, it tracks more than TDS: it covers mutual funds, property deals, and foreign remittances.
Consider it a refined portfolio that captures your complete financial journey. All of this is packed into a single, easy-to-navigate report.
The AIS brings together income from various sources, tax deductions, high-value transactions, and financial dealings into one unified view. By boosting transparency and making hidden income harder to slip, AIS tackles tax evasion head-on.
Automate your compliance workflow. Integrate AIS data into your accounting software with Registerkaro’s guidance. Get in touch today!
Importance of Your Annual Information Statement
The annual information statement empowers businesses with a unified financial overview for accurate compliance and strategic tax planning, among others, as follows:
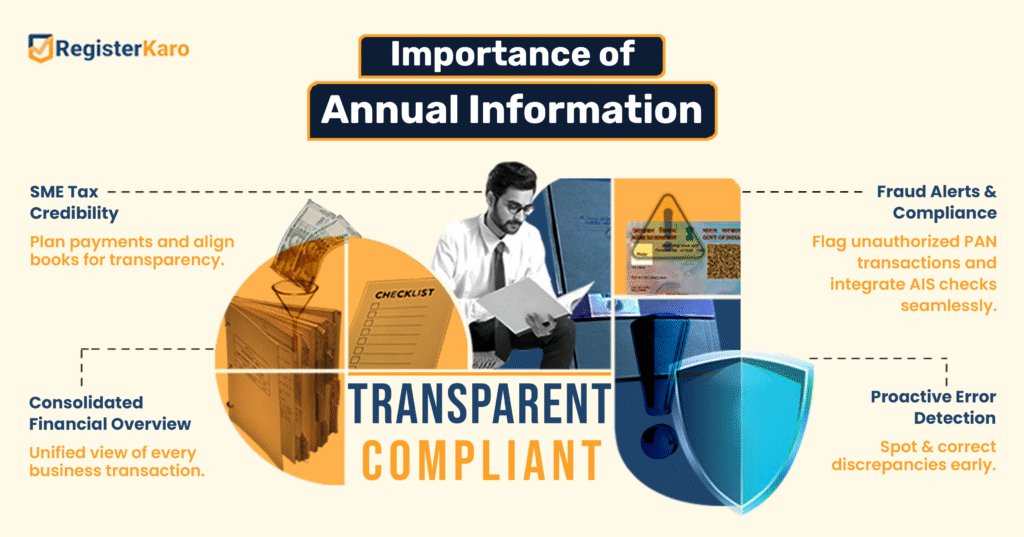
- AIS offers a consolidated view of all your business’s financial transactions, acting as your defense against tax discrepancies. Regular reviews of your AIS help you spot and correct errors before they escalate into costly compliance issues.
- For MSME registration, AIS delivers invaluable insights into income sources and investment returns. Armed with this data, you can anticipate potential tax liabilities and plan payments proactively, avoiding last-minute surprises.
- AIS enhances transparency between taxpayers and the IT department by aligning your internal records with officially reported data. This boosts your credibility and reduces the likelihood of scrutiny notices or audits.
- The statement also flags any unauthorized transactions linked to your PAN, enabling swift detection of fraud or identity theft. Early identification of suspicious entries lets you take immediate action to safeguard your finances.
- By integrating AIS checks into your regular financial review process, you establish a robust framework for ongoing tax compliance. This routine streamlines your tax filings and strengthens your strategic financial planning.
Now that you’ve seen the impact of AIS checks on compliance, let’s walk through the steps to grab it online.
How to Access Your Annual Information Statement?
Here’s how you can quickly access your annual information statement:
| Step | What You’ll Do |
| 1. Hop onto the e-filing portal | Head over to www.incometax.gov.in and log in with your user ID and password. You’re entering the income tax department’s digital lobby, no secret handshake needed! |
| 2. Point and click to AIS | Click the Services tab and choose Annual Information Statement (AIS) from the dropdown. It’s like picking your favorite flavor at an ice-cream counter. |
| 3. Choose your year | On the AIS dashboard, pick the assessment year you want to explore; your financial time machine awaits. Then hit download to grab your statement in PDF form. |
| 4. Separate PAN | If you juggle multiple entities, remember each PAN has its own AIS playground. Log in separately for each, so no business party crashes another’s data. |
| 5. Easy Access | The portal’s mobile-friendly interface means you can review your AIS from anywhere, even during your coffee run. Tech-savvy tax checks, right in your pocket. |
| 6. Review | Scan your AIS regularly to catch any sneaky discrepancies before they grow into full-blown dramas. Staying on top now saves you tax headaches later! |
Crucial Components of Annual Information Statement
The annual information statement contains several key sections that provide a comprehensive view of your financial activities. Understanding these components helps you analyze your financial data more effectively:
- Income Information: This section lists income from various sources, including salary, interest, dividends, and professional fees. For businesses, it shows receipts from customers with TDS deductions.
- Tax Payment Details: The annual information statement tracks advance tax payments, self-assessment tax, and TDS/TCS credits. This helps verify that all tax payments are correctly reflected in the system.
- Financial Transactions: High-value purchases, property transactions, investments, and foreign remittances appear here. This part of the annual information statement helps track significant financial movements.
- Tax Deductions: All deductions claimed under various sections of the IT Act, including charitable donations and investments in tax-saving instruments, are recorded.
- Pending/Completed Proceedings: Information about ongoing assessments, appeals, or other tax-related proceedings appears in this section of the annual information statement.
- Demand and Refund: Details about outstanding tax demands or pending refunds help manage your cash flow expectations.
- Specified Financial Transactions (SFT): This critical component tracks high-value transactions like property purchases, bank deposits, credit card payments, and mutual fund investments.
Each component of the annual information statement serves a specific purpose in ensuring complete financial transparency.
With your records aligned, it’s useful to compare Form 26AS and the AIS side by side to understand the full scope of your reported transactions. This contrast highlights where each report fits into your compliance toolkit.
Difference Between Form 26AS and Annual Information Statement
A quick look at Form 26AS and the annual information statement together:
| Aspect | Form 26AS | Annual Information Statement |
| Scope & Purpose | Focuses on tax deduction and collection: TDS/TCS credits, advance tax, and self-assessment tax payments. | The annual information statement income tax return provides a comprehensive view of financial transactions, including items beyond tax credits. |
| Data Included | TDS/TCS credits, advance tax, and self-assessment tax. | All Form 26AS data plus foreign remittances, high-value transactions, mutual-fund investments, and other specified financial events. |
| Update Frequency | Updated after the tax department processes and confirms credits. | Updated more frequently with raw transaction data from banks, financial institutions, and other reporting entities. |
| Business Insights | Helps verify tax credits and payments made. | Offers detailed insights into customer transactions and financial activities, aiding in book reconciliation and forensic analysis. |
| Usage | Essential for confirming tax credits. | Combining with Form 26AS to give a full picture of tax-related financial activities, detecting unreported income or mismatches across both documents. |
Now that you’ve mapped out how Form 26AS and your AIS complement each other, it’s time to dive in and verify each AIS entry against your records.
How to Verify Information in Your Annual Information Statement?
Regular verification of your annual information statement helps prevent compliance issues. Follow these practical steps to check your statement effectively:
- Download and Match
Grab your AIS PDF from the Income Tax portal and line it up against your books like a financial detective. Scrutinize each income source, especially customer payments with TDS, to make sure every rupee is accounted for. - Validate Your Tax Credits
Reconcile your tax payments by cross-referencing AIS entries with payment receipts and bank statements. Flag and fix any missing or inaccurate credits before they trip you up during filing. - Inspect High-Value Transactions
Dive into the SFT section to confirm that big-ticket dealings mirror your actual transactions. If you spot unfamiliar entries, treat them like red flags and investigate errors or fraud right away. - Report Discrepancies Instantly
Use the AIS feedback tool to tag each entry as correct, partially correct, or incorrect; no more waiting for tax-time surprises. Prompt reporting accelerates resolution and keeps your records squeaky clean. - Reconcile with Your Accountant
Team up with your accountant to align AIS data with your GST returns and financial statements. This three-way match makes sure you’re compliant and audit-ready, without any nasty gaps. - Quarterly Check-Ins
Swap the annual scramble for quarterly quick looks, set a reminder, and make AIS reviews part of your routine.
With Registerkaro handling your AIS reconciliation, let’s explore common AIS hiccups and simple fixes.
Common Issues with Annual Information Statement and Their Solutions
Businesses often face several challenges when dealing with their annual information statement. Here are common issues and practical solutions:
1. Duplicate Entries: Sometimes, the annual information statement shows the same transaction multiple times.
Solution: Flag these duplicates using the feedback option on the portal. Keep records of the original transaction to support your claim.
2. Missing Transactions: When expected income or tax credits don’t appear in your annual information statement.
Solution: Check if the reporting entity has submitted the correct details. If confirmed, contact your tax professional to help address the issue with the appropriate authorities.
3. Incorrect Amounts: Amounts in the annual information statement differ from your actual transactions.
Solution: Submit corrected information through the portal’s feedback mechanism. Attach supporting documents like bank statements or invoices.
4. Annual Information Statement Login Problems: Technical issues when trying to access your statement.
Solution: Clear browser cache, use supported browsers, or try accessing during non-peak hours. The income tax helpdesk can assist with persistent login problems.
5. Information Processing Delays: Recent transactions are missing from your annual information statement.
Solution: Allow sufficient processing time (usually 30-60 days) before reporting missing entries. Regular monitoring helps track when new information appears.
6. Third-Party Reporting Errors: When financial institutions report incorrect information.
Solution: Contact the reporting entity first to correct the information at the source. Then follow up with updates to your annual information statement.
Having addressed those AIS hiccups, it’s time to adopt a solid routine of best practices. This approach keeps your AIS data accurate, organized, and always audit-ready.
Best Practices for Managing Your Annual Information Statement
Set up quarterly AIS reviews to spot and resolve discrepancies early. Use a focused checklist for verifying income, tax payments, and high-value transactions. Maintain organized records: receipts, invoices, bank statements, sorted by month. These documents prove invaluable when contesting incorrect AIS entries.
Leverage accounting software that imports AIS data for automated transaction matching. Train your finance team on AIS importance and assign clear monitoring responsibilities. Review your AIS with a tax professional before filing to uncover hidden liabilities. Track all AIS feedback submissions and follow up to build a paper trail of due diligence.
Protect your business from surprises! Use Registerkaro’s AIS service to flag unauthorized or missing transactions. Catch issues early and avoid penalties down the road.
Final Thoughts on Understanding the Annual Information Statement
Ditch the last-minute panic and make AIS checks a quarterly ritual; your books will thank you. With a clear rundown of every TDS return, credit, high-value deal, and remittance, you’ll spot mismatches faster than you can say “compliance.”
Think of AIS as your financial crystal ball: it keeps the tax department smiling and highlights growth opportunities you might’ve missed. Logging in the portal is all it takes to review your AIS, and with automated accounting, transactions feels more like magic than math.
Chat with RegisterKaro to iron out hidden liabilities and strategize smarter tax moves. Embrace AIS as more than a formality, it’s your roadmap to sharper financial planning and smoother compliance!
Frequently Asked Questions
AIS pulls raw RBI data on outward remittances as soon as banks report them. This lets you spot unreported fund transfers before filing your return.


























