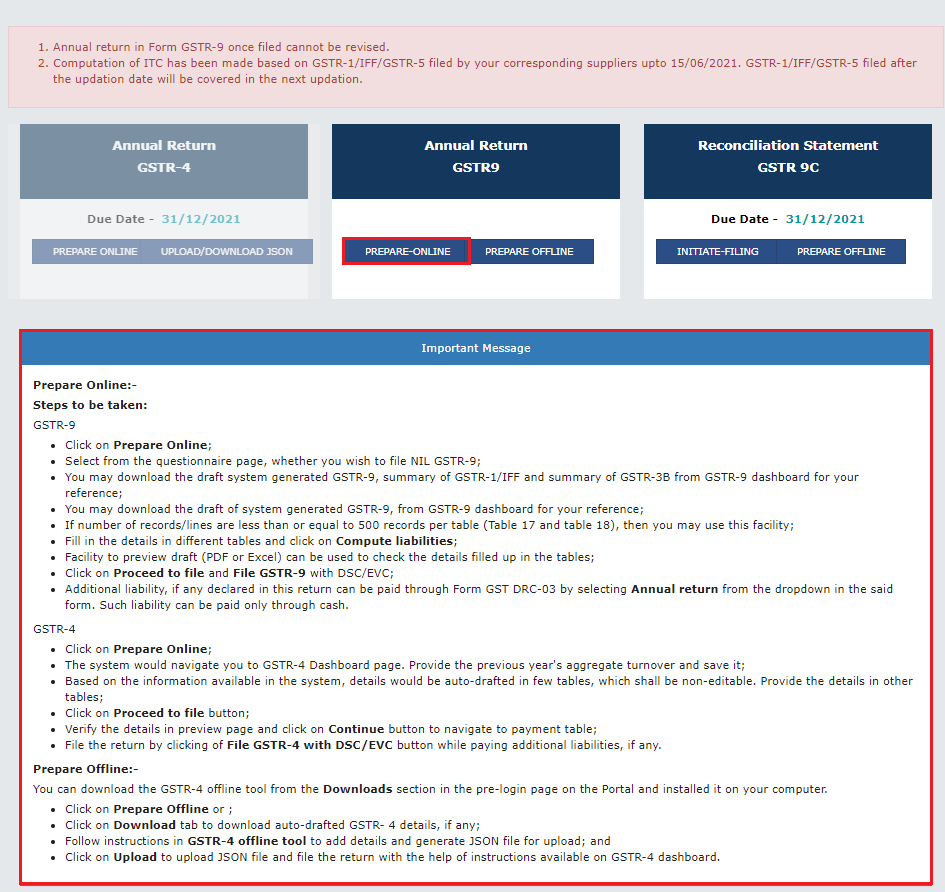
GSTR-9 is an annual return that GST-registered persons are required to submit at the close of every financial year. It provides a detailed summary of all GST transactions reported through monthly or quarterly returns like GSTR-1 (outward supplies) and GSTR-3B (summary return).
The form includes details of:
- Sales and purchases made during the financial year,
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) claimed and reversed,
- Taxes paid under Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST), State Goods and Services Tax (SGST), Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST), and Cess,
- Interest, refunds, and demand adjustments (if any).
Purpose of Filing GSTR-9
The main reasons for filing GSTR-9 are to:
- Match data: Align information reported in monthly/quarterly returns (GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B) with the taxpayer's yearly financial records.
- Ensure compliance: Provide a full yearly declaration of GST transactions with all GST laws.
- Identify discrepancies: Assist taxpayers and authorities in detecting errors or inconsistencies in previously filed GST returns.
- Summarise data: Provide a concise, unified summary of all GST transactions for the entire financial year.
Different Forms Under GSTR-9 Annual Return
While GSTR-9 is the main annual return form under GST, there are a few related forms designed for different types of taxpayers and reporting needs. Each serves a specific purpose depending on the taxpayer’s registration type, turnover, and role in the GST system.
Here’s a breakdown of the different forms:
- GSTR-9: This is the standard annual return form for regular taxpayers registered under GST. It includes consolidated details of outward and inward supplies, ITC, tax paid, and other related information for the full financial year.
- GSTR-9B: This form is an annual statement for e-commerce operators who collect Tax at Source (TCS) and file Form GSTR-8. It is intended to be a consolidated summary of all TCS collected by the operator during the financial year.
- Note: The requirement to file GSTR-9B has been deferred by the government since its introduction. Therefore, e-commerce operators are currently not required to file it.
- GSTR-9C: This is a reconciliation statement for taxpayers whose annual turnover exceeds Rs. 5 crores (applicable from FY 2020–21 onwards; earlier the limit was Rs. 2 crore).
It includes:
- A comparison between the data filed in GSTR-9 and the audited financial statements.
- The form must be self-certified by the taxpayer (audit by a CA or CMA was required earlier, but is now optional).
- Helps ensure transparency and accuracy in reporting.
Choosing the right form and understanding your GSTR-9 filing eligibility is essential to ensure error-free annual return filing under GST.
Note: GSTR-9A has been suspended and replaced by GSTR-4 for annual filing from FY 2019-20 onwards. This form is meant for taxpayers under the Composition Scheme, which allows small businesses to pay tax at a fixed rate.