
Goods like machines and industrial equipment are valued for their performance, precision, and quality in the market. A trusted brand provides the buyers with consistent quality and support. Businesses can maintain the uniqueness of their products and brand identity by registering under Trademark Class 7. It ensures legal protection of their brand against imitation and misuse.
In India, trademark registration follows the Nice Classification system to ensure standardized legal protection for brands. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) established the NICE Classification through the NICE agreement in 1957. Its main goal was to create a globally recognized framework for categorizing goods and services.
For clarity, it divided products and services into 45 different trademark classes:
- Class 1-34: Goods, including machinery, industrial tools, and other products
- Class 35-45: Services, such as finance, education, and business support
This system helps businesses understand the proper legal classification for their goods and services. Hence, it ensures correct trademark registration and reduces errors.
What is Trademark Class 7 in India?
Trademark Class 7 covers industrial and mechanical machines, including motors, engines, construction & manufacturing tools. Under the NICE Classification class 7, a trademark protects brands selling machinery and industrial equipment. It gives them exclusive rights to use their brand and prevents imitation.
In India, trademark registration follows the Trade Marks Act, 1999. The Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trade Marks (CGPDTM) oversees the process through the Trade Marks Registry.
The Registry uses the NICE Classification system to maintain clear and consistent protection for goods and services.
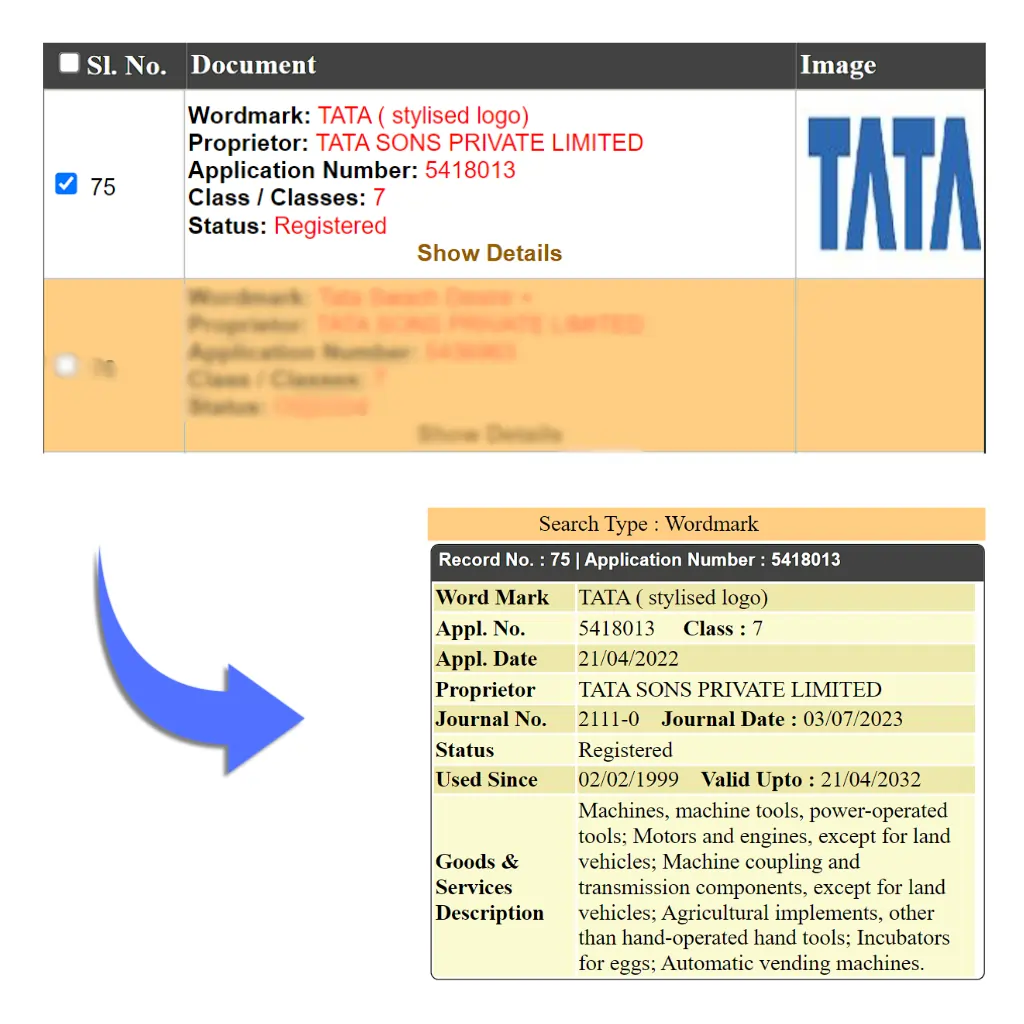
A notable example of a Class 7 trademark in India is Kirloskar. They manufacture pumps, engines, and industrial machines protected under this class.
Who Should Choose Class 7 Trademark in India?
Businesses dealing with industrial machines, motors, and mechanical equipment should consider registering under Class 7. The following types of companies and sellers can benefit from Class 7 trademark protection:
- Industrial machine manufacturers: Class 7 covers machinery trademark registration in India. It includes Companies producing motors, engines, pumps, and heavy machinery.
- Construction equipment brands: Sellers of excavators, loaders, concrete mixers, and other construction machines.
- Manufacturing tool companies: Brands making machine tools for cutting, shaping, or finishing materials.
- Agricultural machinery manufacturers: Businesses producing tractors, harvesters, seeders, and ploughing equipment.
- Food and textile machinery makers: Companies offering industrial mixers, grinders, textile spinning, or weaving machines.
- Packaging and printing equipment brands: Sellers of bottling, labeling, and printing machines.
- Mining and earth-moving equipment companies: Businesses dealing in industrial loaders, crushers, and mining machinery.
Proper registration under trademark class 7 helps prevent disputes and strengthens the brand’s position as a trusted manufacturer or seller.
What Goods Fall Under Trademark Class 7?
Trademark Class 7 mainly covers trademark registration for machines, mechanical tools, and industrial equipment. This class includes devices used in manufacturing, construction, agriculture, food processing, and other industries.
The table below highlights the trademark class 7 goods list:
| Goods Type | Description | Examples |
| Industrial machines | Machines used in factories or production units | Motors, pumps, engines, and assembly line machines |
| Construction equipment | Machines used in construction and civil work | Excavators, loaders, concrete mixers, and bulldozers |
| Manufacturing tools | Tools and machines for shaping, cutting, or finishing materials | Lathes, drills, presses, and milling machines |
| Agricultural machinery | Equipment for farming and crop production | Tractors, harvesters, ploughs, and seeders |
| Food processing machines | Machines used for grinding, mixing, or preparing food | Industrial mixers, grinders, and slicers |
| Textile and garment machinery | Machines used in textile production and garment manufacturing | Spinning machines, weaving machines, and sewing machines |
| Packaging and printing machines | Machines for packaging, labeling, or printing products | Bottle fillers, labeling machines, and printing presses |
| Mining and earth-moving equipment | Heavy machines for excavation and mining operations | Crushers, industrial loaders, and mining shovels |
To ensure the registration of your goods under the right trademark class, contact RegisterKaro today. We offer expert guidance, accurate filings, and complete support to secure your brand and stay ahead of competitors.
What is Not Covered in Trademark Class 7?
Many businesses assume certain equipment or tools fall under Class 7, but they actually belong to other trademark classes. Choosing the right class avoids objections and unnecessary re-filing. The table below highlights goods not covered under Trademark Class 7 and their correct classes:
| Goods Type | Examples | Correct Class |
| Hand tools | Manual hammers, screwdrivers, wrenches | Class 8 |
| Household appliances | Electric kettles, fans, and air conditioners | Class 11 |
| Vehicles and transport | Cars, motorcycles, bicycles | Class 12 |
| Measuring instruments | Scales, thermometers, gauges | Class 9 |
| Food processing equipment for home use | Small grinders, mixers | Class 21 |
| Office machinery | Printers, photocopiers, calculators | Class 16 or Class 9 |
| Safety and protective gear | Helmets, gloves, protective clothing | Class 9 or Class 10 |
Tip: Use RegisterKaro’s free Trademark Class Search Tool to identify the right class for your services.
How to Register a Class 7 Trademark in India? Step-by-Step Guide
Registering a trademark under Class 7 protects machines, industrial equipment, and mechanical tools from unauthorized use. You can apply whether the trademark is already in use or intended for future use.
Step 1: Preparation Before Filing
Trademark Search:
Check if your desired brand name or logo is already registered under Class 7 using the IP India portal or the RegisterKaro Trademark Search Tool. This avoids conflicts with existing trademarks.
Define Product Details:
List the machines and equipment clearly, such as motors, industrial mixers, construction machinery, or agricultural tools. Avoid vague or overly broad descriptions.
Step 2: Application Submission
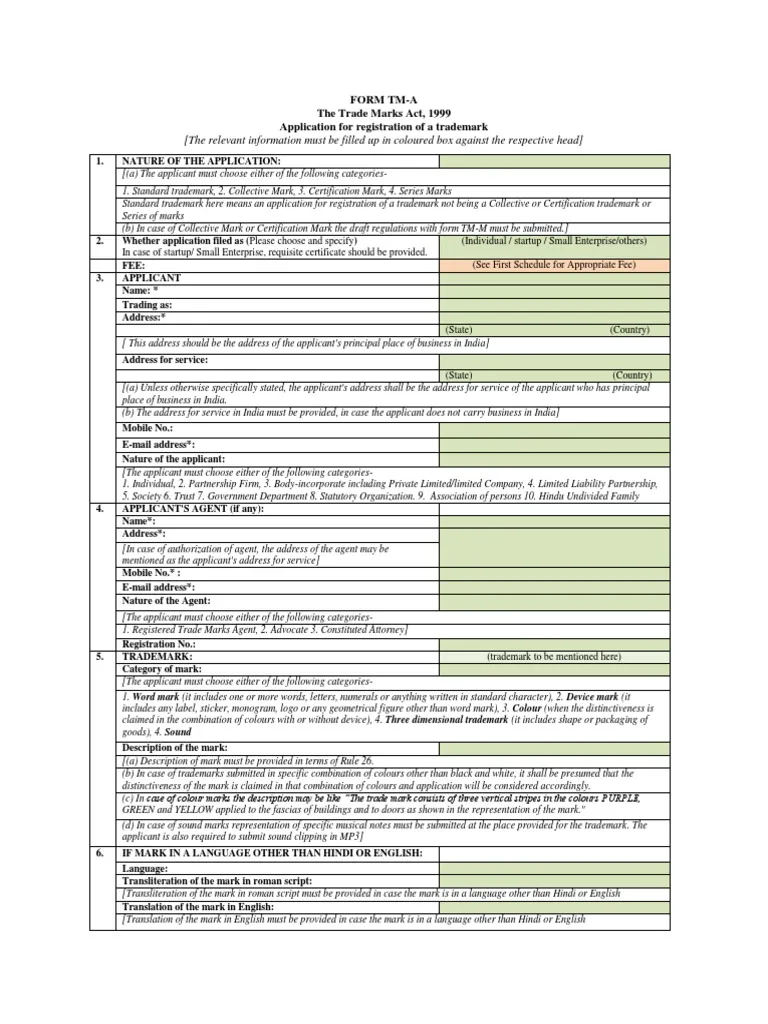
Filing Form TM-A:
Submit your trademark application online through the IP India Trademark Portal.
Government Fees (Approximate):
- Individuals, startups, MSMEs: Rs. 4,500 per class
- Companies and other entities: Rs. 9,000 per class
Single-Class vs. Multi-Class Filing:
- Single-class application: Covers only Class 7 goods.
- Multi-class application: Suitable if your brand also deals with products in other classes (e.g., Class 8 for hand tools).
Step 3: Examination and Publication
Examination:
The Trademark Registry reviews the application for correct classification, distinctiveness, and similarity with existing trademarks. If there are issues, an Examination Report is issued.
Respond to Objections:
You must reply to Trademark objections within 30 days.
Trademark Journal Publication:
Once approved, the mark is published in the Trademark Journal for four months. During this period, third parties may raise a Trademark opposition.
Expected Timeline:
The examination typically takes 6 to 12 months, followed by the 4-month publication period.
Step 4: After Registration
Validity:
A Class 7 trademark is valid for 10 years from the registration date and can be renewed every 10 years.
Brand Monitoring:
Keep an eye on the market to prevent misuse of your brand and take legal action if necessary.
Following the correct steps helps ensure smooth registration and reduces the risk of rejection or legal issues.
Documents Required for Class 7 Trademark Registration
To complete a Class 7 trademark application in India, applicants must submit the following documents:
- Trademark Application (Form TM-A): Include applicant details, trademark information, and a clear list of Class 7 goods.
- Trademark Image: Logo or wordmark exactly as you want it registered.
- Identity Proof: PAN, Aadhaar, or passport for individuals.
- Address Proof: Utility bills, bank statements, or other valid documents.
- Business Registration Proof (if applicable): Certificate of Incorporation, LLP deed, or MSME registration.
- Authorization Letter (Form TM-48): Required if a trademark agent files on your behalf.
- Usage Declaration (if already in use): Mention the first date of use and provide supporting evidence like invoices or product photos.
- Proof of Product Sale or Activity: Catalogs, machine images, packaging, or sales records showing your industrial equipment.
RegisterKaro helps businesses at every stage of Class 7 trademark registration. We handle everything from searching and filing to final approval of your trademark.
Common Mistakes While Registering for Trademark Class 7
Businesses often make several mistakes while registering a Trademark under Class 7 in India. These errors can cause objections, delays, or even rejection of the application.
- Choosing the wrong class: Many businesses confuse Class 7 machines with hand tools or consumer appliances. Manual tools fall under Class 8, and household appliances usually fall under Class 11.
- Using vague product descriptions: Applicants often write broad terms like “machinery” or “industrial equipment.” Using such a description can lead to misunderstanding and increase the chance of objections.
- Skipping a trademark search: Some businesses file without checking existing Class 7 trademarks. This leads to conflicts with similar marks.
- Ignoring brand distinctiveness: Generic or descriptive names often face rejection. Class 7 trademarks must clearly identify the brand, not just the machine type.
- Missing objections or deadlines: Many applicants fail to reply to examination reports within 30 days. This mistake can cause abandonment of the application.
- Not planning for future products: Businesses sometimes register only current machines. Later expansion may need fresh filings. Poor planning increases future costs.
- Filing without professional guidance: Incorrect forms or documents delay approval. Expert support improves accuracy and approval chances.
Registering a Class 7 trademark correctly is essential to protect your machines and industrial equipment from imitation. By avoiding the common mistakes, businesses ensure faster approval and stronger legal protection.
With careful planning and accurate filings, your brand gains credibility and trust in the market. Start your trademark registration today with our professional assistance to secure your business under Trademark Class 7.
Frequently Asked Questions
Trademark Class 7 in India covers machines, mechanical tools, and industrial equipment. This includes devices used in manufacturing, construction, agriculture, food processing, and packaging. It also applies to motors, engines, pumps, and other powered equipment that are not intended for vehicles. Following the NICE Classification system, Class 7 helps businesses protect their machinery brands and ensures that competitors cannot use similar marks for the same category of industrial products.




