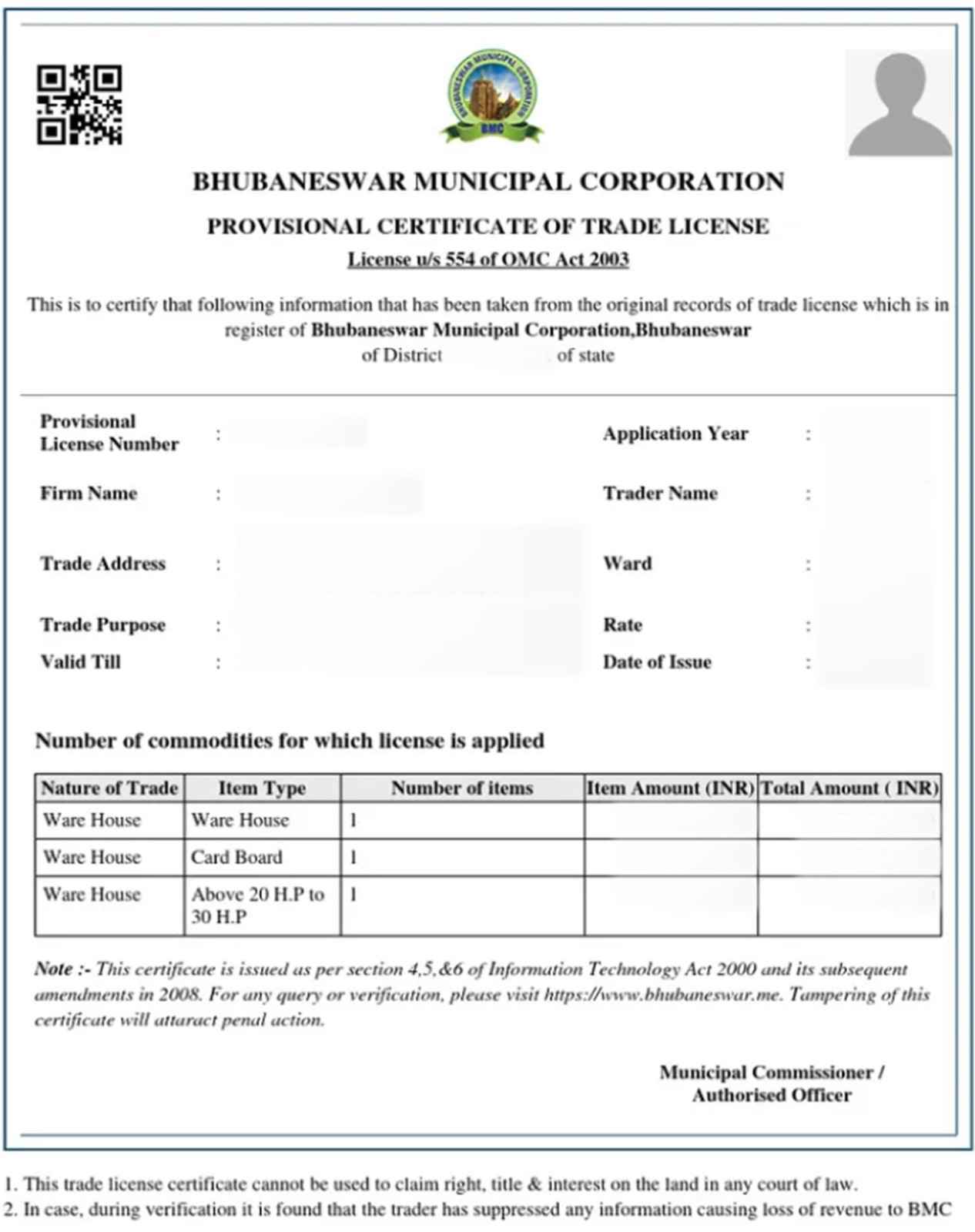
Obtaining a Trade License in Odisha is governed by specific state and local regulations that vary depending on the nature of the business and its location. While the core purpose of the license remains consistent, the details of the process are highly localized.
Odisha Municipal Corporation/Local Body and Trade License
In Odisha, the authority to issue trade licenses is vested in the respective Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), which include Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, and Notified Area Councils (NACs), as well as Panchayats for rural areas.
In major cities like Bhubaneswar and Cuttack, the process is managed by their respective Municipal Corporations, such as the Bhubaneswar Municipal Corporation (BMC) and the Cuttack Municipal Corporation (CMC). These bodies operate under the Orissa Municipal Corporation Act, 2003, and their own by-laws, which dictate specific application forms, required documents, and fee structures. For other towns, the local Municipal Board or NAC handles the licensing.
A key local angle is the SUJOG portal (sujog.odisha.gov.in), which serves as a unified online platform for citizens to access various services, including trade license applications and renewals, for most ULBs in the state.
Specific Industries Requiring Special Trade Licenses
Certain businesses in Odisha are considered high-risk or require a higher level of scrutiny due to their nature. These industries need to obtain specific types of trade licenses in addition to the general license. Examples include:
- Food and Health Establishments: Businesses such as restaurants, hotels, hospitals, and food processors require a Health Trade License. They must comply with strict hygiene and sanitation standards set by the local ULB. Additionally, they must obtain a license from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), which is mandatory for all food business operators.
- Industrial and Manufacturing Units: Factories and production units need a specific Industrial Trade License. They are also required to obtain a Consent to Establish (CTE) and Consent to Operate (CTO) from the Odisha State Pollution Control Board (OSPCB) to ensure they meet environmental safety standards.
- High-Risk Trades: Businesses involved in activities like handling hazardous chemicals, storing flammable materials, or operating workshops with high-power machinery may be classified under a "Hot Work Category License" or similar special permits, which often require a separate NOC from the Fire Department and the OSPCB.
Recent Changes or Updates in Trade License Rules for Odisha
The government of Odisha has been making efforts to simplify the process and improve the ease of doing business. Recent updates include:
- Online Systems: The shift to online portals like SUJOG has made the application and renewal process faster and more transparent. These platforms also allow for online fee payments and the digital issuance of licenses, often with QR codes for instant verification.
- Waiver of Renewal for Shops and Establishments: A recent draft notification proposes to get rid of the requirement to renew the registration of shops and commercial establishments regularly, with the license remaining valid until revoked. However, the trade license itself must still be renewed annually, usually by March 31st.
- Incentives for Using Odia Language: To promote the use of the local language, the Odisha government has offered a 5% discount on the trade license renewal fee for businesses that prominently use the Odia script on their signboards. This is part of the state's initiative to ensure compliance with the Odisha Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1956, which mandates the use of Odia on signboards.