
“A great product wins hearts, but a great name can win the world.” Imagine your creamy yogurt, golden butter, or crispy snacks sitting on shelves next to dozens of competitors. How do you ensure customers choose yours? One way to do that is by protecting your brand name and identity. That’s exactly where trademark Class 29 steps in.
Trademark Class 29 doesn’t just protect processed and preserved food products; it preserves your story, your reputation, and your hard-earned identity.
When products look alike, and customers subconsciously purchase your products, your brand name becomes your strongest asset. Trademark registration ensures that customers instantly recognize your products, trust your quality, and keep returning. This blog guides you through how trademark Class 29 helps secure that identity.
Class 29 of Trademark Overview: Meaning and Scope
Trademark Class 29 is part of the international system for classifying goods under trademarks. It focuses on edible and processed food products, helping businesses protect their brand identity in the food and beverage sector.
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) manages the Nice Classification (NCL), an international standard for classifying goods. The Nice Classification divides all goods and services into 45 different trademark classes: 34 for goods and 11 for services. This standard ensures global consistency and allows businesses to simplify international trademark protection.
In India, the Trade Marks Act, 1999, governs trademarks. The Act aligns with international practices like the Nice Classification. It allows individuals and companies to register trademarks to protect their brand names, logos, and product identity. Registering a trademark under Class 29 gives businesses exclusive rights over their edible products.
For example, Nestlé protects its dairy products, processed foods, and packaged edible items under this class, preventing competitors from using similar brand identities.
By registering under this trademark class, food and beverage businesses can enjoy several benefits, including:
- Exclusive brand rights: Gain the sole right to use your brand for edible and processed food products.
- Protection against imitation: Prevent competitors from copying or misusing your brand.
- Enhanced customer trust: Build credibility and loyalty through a recognized and protected brand.
- Market distinction: Stand out in a crowded food and beverage market and reduce confusion.
- Business growth opportunities: Facilitate licensing, franchising, and expansion domestically and internationally.
- Legal enforcement: Take action against trademark infringement and safeguard your intellectual property.
- Ease of franchising: Simplify franchising or licensing by legally securing your brand across locations.
These advantages make registering under the trademark class for meat a smart move for any business looking to protect and grow its brand.
Who Should Register Under Class 29?
Not every business needs the same trademark protection. But if your brand deals with food products that customers consume daily, then you should register under Class 29.
- Food manufacturers and processors producing packaged, frozen, or preserved food items
- Dairy brands offering milk, butter, cheese, yogurt, or related products
- Meat, fish, and poultry suppliers selling fresh or processed goods
- Edible oil and fat producers, including cooking oils, ghee, and margarine
- Snack and packaged food brands operating in the ready-to-eat or processed food space
- Health and nutrition brands selling protein-based or food-derived products
- Private label food brands selling store-branded dairy, frozen, or packaged food products
- Export-oriented food businesses supplying processed or preserved food to international markets
- Cold storage and frozen food companies selling ready-to-cook or frozen edible items under their own brand
- Online and D2C food brands, including cloud kitchens, are offering packaged or branded food products through e-commerce platforms
- Organic and specialty food brands focusing on plant-based, preservative-free, or premium food products
- Agricultural processing units convert raw produce into packaged or preserved food items
- Co-operative societies and food federations marketing dairy or processed food products under a common brand
- White-label manufacturers producing branded edible goods for third parties
Whether you operate locally or sell across states, registering under the correct class is a strategic necessity.
Products Covered Under Trademark Class 29: Detailed List
If your food product requires processing or preservation before reaching consumers, it is likely classified under this category. Here is a list of products covered under Class 29 of the trademark:
| Product Category | Examples of Goods Covered |
| Meat & Poultry Products | Fresh, frozen, dried, cooked meat; poultry; meat extracts |
| Fish & Seafood | Fish, shellfish, crustaceans, preserved and processed seafood |
| Dairy Products | Milk, cheese, butter, yogurt, cream, ghee, paneer |
| Milk Substitutes & Dairy Alternatives | Soy milk, almond milk, coconut milk (for food use) |
| Eggs & Egg Products | Eggs, egg powder, processed egg-based foods |
| Edible Oils & Fats | Cooking oils, vegetable oils, margarine, edible fats |
| Preserved Fruits | Jams, jellies, fruit preserves, canned fruits |
| Preserved Vegetables | Pickles, canned vegetables, preserved garlic, onions, and ginger |
| Processed Legumes & Pulses | Canned beans, lentils, chickpeas |
| Processed Nuts & Seeds | Roasted nuts, nut butters, seed-based spreads |
| Frozen & Ready-to-Cook Foods | Frozen meals, ready-to-cook packaged foods |
| Prepared Soups & Broths | Meat-based soups, vegetable soups, bone broths |
| Protein-Based Food Products | Food-based protein products of animal or plant origin |
| Gelatin & Collagen (Food Use) | Edible gelatin, food-grade collagen |
| Tofu & Soy-Based Products | Tofu, soy curd, soy-based meat substitutes |
| Mushrooms & Truffles (Processed) | Canned or preserved mushrooms and truffles |
| Baby Food (Food-Based) | Dairy-based or meat-based baby food products |
| Snack-Based Processed Foods | Potato chips, vegetable-based processed snacks |
Need expert help with Trademark Class 29 registration? RegisterKaro helps you identify the correct classification and product description, so your trademark application accurately reflects your business. Contact us today and get expert guidance on the trademark class for dry fruits registration!
Products Not Covered Under Trademark Class 29
Trademark Class 29 does not cover all food-related products. Some items that appear similar may fall under different trademark classes based on their composition, level of processing, or intended use.
The following products are not covered under Trademark Class 29:
- Raw agricultural produce such as fresh fruits, fresh vegetables, grains, cereals, and unprocessed pulses (Class 31)
- Cereal-based and bakery products, including bread, biscuits, cakes, pastries, pasta, noodles, and pizzas (Class 30)
- Confectionery and sweet products such as chocolates, candies, toffees, chewing gum, and sugar-based items (Class 30)
- Beverages of all kinds, including fruit juices, soft drinks, mineral water, energy drinks, tea, coffee, and alcoholic beverages (Classes 32 and 33)
- Fresh or live food items like live animals, live fish, and unprocessed meat (Class 31)
- Spices, condiments, and seasonings such as salt, pepper, sauces, and flavorings (Class 30)
- Dietary supplements and medicinal food products with therapeutic claims (Classes 5 or 30, depending on composition)
Filing your trademark under the wrong class can delay registration, cause unnecessary objections, and weaken your brand’s legal protection. Use RegisterKaro’s free trademark class search tool to promptly identify the right class for your products.
How to File a Trademark Under Class 29 in India?
Registering a trademark under Class 29 follows a defined legal process under the Trade Marks Act, 1999. You can file under either “proposed to be used” if your brand is not yet operational, or “already in use” if the products are already in the market.
Here’s the step-by-step process to register a trademark class for dry fruits:
- Conduct a Trademark Search: Search the IP India database or use RegisterKaro’s trademark name availability check tool to check if a similar trademark exists.
- Select the Correct Class and Product Description: Choose Class 29 for processed or preserved food products of animal origin. Accurately describe each product and avoid vague terms. If your products span other categories, consider multi-class filing.
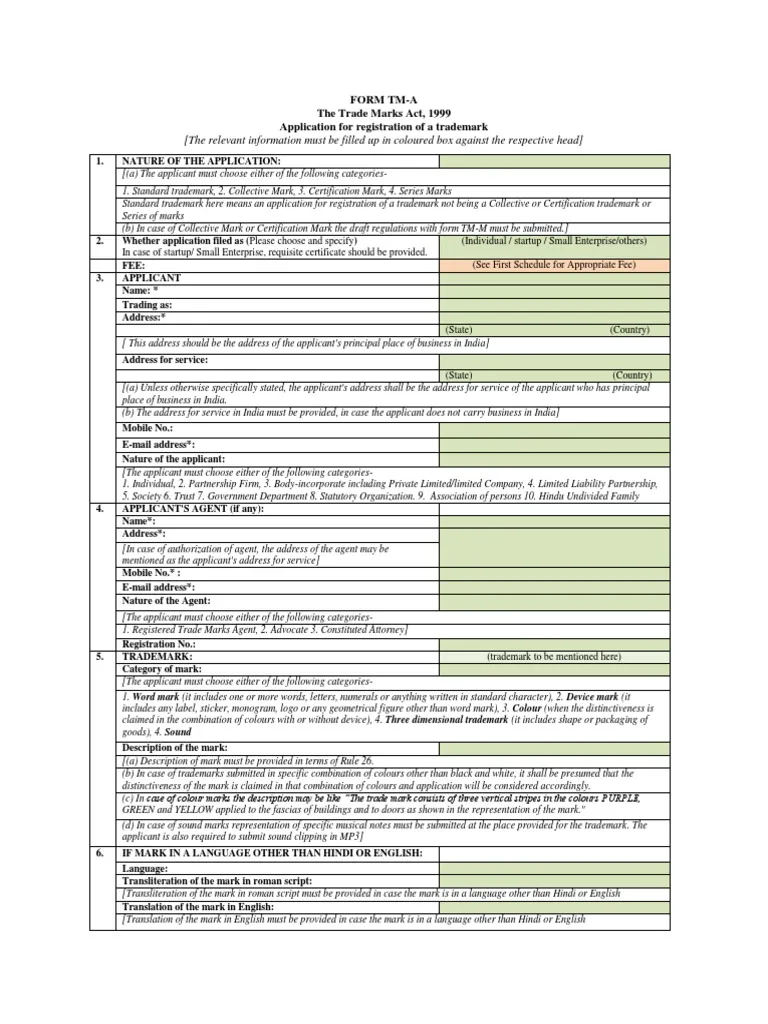
- File the Trademark Application (Form TM-A): Submit Form TM-A with all details:
- applicant’s name
- Business address
- Trademark type
- Logo or wordmark
- Examination by the Trademark Registry: The Registrar checks your application for legal compliance, similarity to existing marks, and distinctiveness. Respond to trademark objections (usually within one month) with clarifications or evidence.
- Publication in the Trademark Journal: After examination, the Trademark Registry publishes trademark applications in the Trademark Journal. The public has four months to oppose the trademark.
- Trademark Registration and Certificate Issuance: Once the Registrar clears your application, they issue the official registration certificate. Use the ® symbol to signify registered status.
- Trademark Renewal: Renew your trademark every ten years. File trademark renewal before the expiry date to maintain continuous protection and legal ownership of your brand.
Protect your food brand with RegisterKaro today. Don’t risk delays or errors while filing your trademark under Class 29. We guide you through every step, from conducting a thorough trademark search to filing Form TM-A and handling objections.
Multi-Class Trademark Filing: Classes Related to Class 29
Many food and beverage brands sell products across multiple categories. Filing only under Class 29 in trademark may leave gaps. Multi-class filing protects related products in a single application, saving time and cost while strengthening your brand strategy.
The table below highlights trademark classes related to Class 29, helping you identify where multi-class filing may be necessary for complete brand protection.
| Class Number | Focus Area | Why It’s Relevant |
| Class 30 | Cereals, bakery products, sugar, confectionery, pasta, coffee, tea, and spices | Covers cereal-based and bakery items not included in the trademark class for edible oil |
| Class 31 | Fresh fruits, vegetables, seeds, live plants, unprocessed grains, and agricultural produce | Protects natural and unprocessed food items that Class 29 does not cover |
| Class 32 | Non-alcoholic beverages, mineral water, fruit juices, soft drinks | Secures your rights over drinks made from fruits or other ingredients |
| Class 33 | Alcoholic beverages, including wine, beer, and spirits | Protects alcoholic products associated with your food or beverage brand |
| Class 5 | Dietary supplements, protein powders, and health-focused food products | Covers food items with medicinal or therapeutic claims |
By strategically using multi-class filing, brands enjoy broader protection and reduce the risk of disputes. For example, Amul uses multi-class filing to protect its entire product range. It registers dairy products under Class 29, bakery items under Class 30, and beverages under Class 32 to secure a strong foothold in the competitive food and beverage market.
Class 29 Trademark Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Registering under Class 29 protects your food or edible product brand, but mistakes during the process can delay registration or weaken your rights. Here are common pitfalls and tips to avoid them:
- Choosing the Wrong Trademark Class: Filing under the wrong class, such as Class 30 or 31, which does not match your product. Conduct a thorough trademark search to classify your products correctly under the trademark class for milk.
- Selecting a Non-Distinctive Trademark: Choosing generic or descriptive names like “Fresh Butter” or “Healthy Yogurt.” Choose a unique, memorable word or logo.
- Ignoring Existing Trademarks: Failing to check for similar trademarks can lead to objections or opposition. Conduct a thorough trademark search before filing.
- Choosing the Wrong Type of Trademark: Not understanding the different types of trademarks and selecting the wrong one. Analyze your brand and choose the correct type based on how you present and market your brand.
- Incorrect or Incomplete Product Description: Listing products vaguely or incorrectly on Form TM-A. Accurately describe every product you want to protect.
- Delaying Response to Objections: Ignoring or delaying replies to examination reports or objections from the Trademark Office. Respond within the given timeframe (usually one month).
- Not Monitoring and Enforcing Your Trademark: Assuming registration alone will prevent infringement. Actively monitor competitors, new trademarks, and online platforms.
- Failing to Renew on Time: Letting your trademark lapse by missing the 10-year renewal. Track renewal dates and submit applications early to maintain continuous protection.
- Using Trademark Before Registration: Launching your product without checking availability or filing. Perform a trademark search and file your application before heavy marketing to avoid legal disputes.
Avoiding these common mistakes saves time, cost, and legal trouble.
At RegisterKaro, we handle hundreds of trademark applications under the trademark class for edible oil in India. Our proven process minimizes objections, helps clients avoid common mistakes, and ensures timely registration. We guide food and beverage brands in choosing strong, distinctive trademarks, selecting the right types of trademarks, and classifying goods correctly. With our support, clients secure fast and reliable protection for their edible products and brand identity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Trademark Class 29 is used to protect processed and preserved food products of animal origin. It includes items such as dairy products, meat, poultry, fish, edible oils, fats, and prepared or preserved foods. Registering under this class ensures your brand has exclusive rights and prevents competitors from copying your products or brand identity.




