
Trademark Class 34 helps businesses secure their brand names, logos, and labels associated with tobacco-related goods. This class covers a variety of products, including cigarettes, cigars, electronic cigarettes, smoking papers, pipes, lighters, and related accessories. In India, the Class 34 trademark operates under the Trade Marks Act, 1999.
By registering under Class 34, businesses ensure they prevent misuse, copying, and market confusion. A strong brand identity becomes even more critical in regulated industries like tobacco and smoking products.
This blog simplifies everything you need to know about Trademark Class 34, making it accessible for business owners and beginners. We will explain what Class 34 covers, who can file, and the exact steps to register your tobacco or smoking-related products.
What is a Class 34 Trademark in India?
Trademark Class 34 covers tobacco substitutes, smoking products, and related smoker accessories. This class protects the brand identity under which cigarettes or smoking products reach consumers. Trademark registration does not protect manufacturing methods or formulas but safeguards names and visual brand elements.
Class 34 of trademarks is recognized globally under the Nice Classification system, which organizes trademark categories worldwide. Registering a trademark under this class grants businesses exclusive rights to their brand usage. It also strengthens legal protection against infringement and market competition.
Registration under Class 34 brings several key advantages. It:
- Protects brand identity from copying or misuse in the tobacco market.
- Builds trust among distributors, retailers, and regulatory authorities.
- Provides legal support during disputes or enforcement actions.
- Increases brand value during expansion, licensing, or acquisition plans.
- Helps businesses respond quickly to trademark objections or violations.
- Supports long-term business stability through enforceable ownership rights.
Who Can File for Trademark Class 34 Protection?
Any individual or business dealing with tobacco or smoking products can apply. Manufacturers, wholesalers, exporters, retailers, and brand owners qualify under this class. Startups or businesses can also apply before their launch by filing on a “proposed to be used” basis. You should file under Class 34 trademark in India if you sell or plan to sell:
- Cigarettes, cigars, or cigarillos under a brand name
- Tobacco or tobacco substitutes are not meant for medical use
- Electronic cigarettes or oral vaporizers for smokers
- Smoking accessories like pipes, lighters, or ashtrays
Early filing reduces conflict risks and protects ownership before market exposure.
What Products Does Trademark Class 34 Cover?
The trademark Class 34 item list includes all tobacco products and smoker-related accessories. This coverage ensures businesses protect every product sold under their tobacco brand.
The table below explains the complete Class 34 trademark list thoroughly:
| Category | Products Included Under Class 34 |
| Tobacco Products | Tobacco, chewing tobacco, snuff |
| Cigarettes | Cigarettes, cigarettes with tobacco substitutes, cigarette tips |
| Cigars | Cigars, cigarillos |
| Smoking Papers | Cigarette paper, books of cigarette papers |
| Electronic Smoking | Electronic cigarettes, oral vaporizers for smokers |
| E-Liquids & Flavourings | Liquid solutions, non-essential oil flavourings |
| Smoking Herbs | Herbs for smoking |
| Pipes & Holders | Tobacco pipes, cigarette holders, cigar holders |
| Pipe Accessories | Pipe cleaners, pipe racks |
| Storage Containers | Tobacco jars, tobacco pouches, cigar cases, humidors |
| Smoking Tools | Cigarette cases, cigar cutters |
| Lighting Items | Matches, matchboxes, match holders |
| Lighters & Parts | Lighters, gas containers, lighter wicks |
| Waste Accessories | Ashtrays for smokers, spittoons |
| Rolling Accessories | Pocket machines for rolling cigarettes |
| Hookah Products | Hookahs |
| Mouthpieces | Mouthpieces for cigarette holders |
| Decorative Tips | Amber tips for cigar and cigarette holders |
Need help with your Class 34 trademark registration? Contact RegisterKaro today for expert guidance to secure and protect your brand in India.
Which Products are Not a Part ofTrademark Class 34?
Some related products do not fall under Trademark Class 34 protection. Filing excluded goods incorrectly often causes objections or delayed registration.
Class 34 does not include:
- Tobacco-free cigarettes for medical purposes, which fall under Class 5
- Batteries and chargers for electronic cigarettes, which fall under Class 9
- Ashtrays designed specifically for automobiles, which fall under Class 12
Understanding exclusions ensures accurate filing and stronger compliance with the trademark law.
How to Register Your Trademark in Class 34?
Registering a trademark under Class 34 requires a structured approach that ensures full legal protection. This process applies to both new businesses planning a launch and established brands expanding product lines.
Step 1: Conduct a Trademark Availability Search
Start by confirming that your trademark is unique and not already registered. Use the IP India database or RegisterKaro’s trademark availability search tool. During the search, focus on:
- Existing trademarks under Class 34, including word marks, logos, and slogans
- Phonetic similarities to avoid marks that sound alike but are spelled differently
- Registered and pending applications to prevent conflicts before filing
If conflicts arise, revise your brand name or consult a trademark attorney. This step ensures you avoid future objections, opposition, or legal disputes effectively.
Step 2: Prepare and File Your Trademark Application
Once your trademark is available, prepare Form TM-A for Class 34 filing. Include complete and accurate information to strengthen your application.
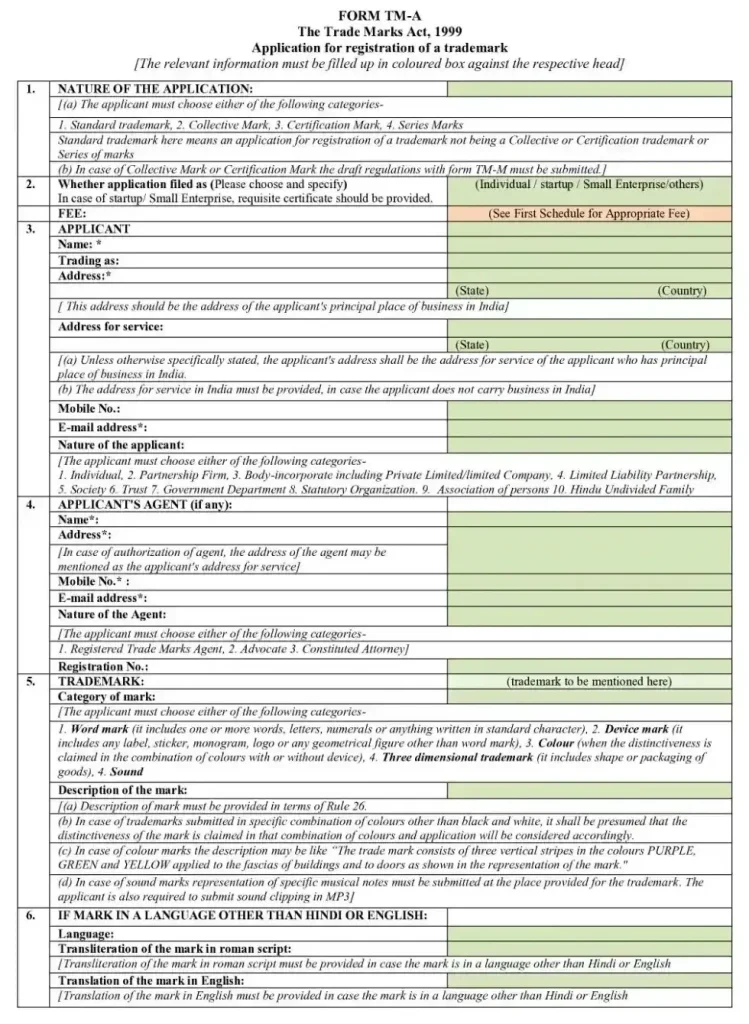
Your application must contain:
- Applicant details (name, address, nationality, and legal entity type)
- Trademark type (word mark, logo, slogan, or combination mark)
- Clear image representation of the logo or wordmark in JPEG format
- Accurate description of all Class 34 products, including tobacco and smoking accessories
- Date of first use, if your brand already operates in the market
- Power of Attorney if filing through an agent, plus proof of use if applicable
Submit your application online using the IP India Trademark E-Filing Portal. The government fee is ₹4,500 for individuals and ₹9,000 for others, depending on the applicant type.
Step 3: Examination by the Trademark Registry
After filing, the trademark examiner reviews your application thoroughly. The examiner checks for distinctiveness and similarity to existing trademarks. Objections may arise under Section 9 (lack of distinctiveness) or Section 11 (similarity with prior marks).
You must respond to trademark objections within 30 days to prevent abandonment. If objections remain unresolved, the registry may schedule a trademark hearing to discuss your case further.
Step 4: Publication in the Trademark Journal
After a successful examination, the registry publishes your mark in the Trademark Journal. Publication opens a four-month opposition period for third parties to challenge your trademark. If no opposition succeeds, your application moves to final registration without delay.
Step 5: Final Registration and Ongoing Protection
The registry issues a registration certificate granting exclusive rights for your trademark. You can use the ® symbol legally once the trademark is registered under Class 34. The registration remains valid for 10 years, and timely trademark renewal ensures continuous protection.
Following these steps thoroughly helps businesses avoid objections, legal disputes, and infringement issues.
Ready to secure your brand under Trademark Class 34? RegisterKaro guides you through every step, from conducting a trademark search to obtaining your registration certificate, helping you avoid errors.
Which Other Trademark Classes Create Confusion With Class 34?
Many applicants confuse trademark Class 34 with other classes because tobacco-related products often connect with devices, health claims, or usage environments. This misunderstanding typically occurs when businesses focus on product function instead of trademark classification rules. The most common confusion arises with the following trademark classes:
- Class 5: Class 5 covers medicinal or therapeutic nicotine products intended for health or treatment purposes. Businesses selling nicotine gums, patches, or medical cessation products must file under Class 5. Trademark Class 34 only covers tobacco substitutes not meant for medical use.
- Class 9: Trademark Class 9 protects electronic devices, batteries, chargers, and software–based products. E-cigarette devices, chargers, and electronic components fall under Class 9 protection. Trademark Class 34 only protects e-cigarettes and vaporizers as smoking articles, not electronics.
Note: Although Class 34 includes e-cigarettes and vaporizers, their manufacture and distribution are banned in India under the Prohibition of Electronic Cigarettes Act, 2019. Businesses can still register trademarks for brand protection or international use.
- Class 12: Class 12 covers accessories designed specifically for vehicles and automobiles. Ashtrays made for cars fall under Class 12, not under trademark Class 34. Regular smoker ashtrays without vehicle design stay protected under Class 34.
Many businesses file multiple trademark applications to protect every product category properly. This approach works especially well when brands sell tobacco products along with electronic devices. Multi-class filing reduces legal gaps and strengthens protection across different trademark classes.
For example, Philip Morris International uses multi-class trademark filing to protect its diverse product range. The company registers traditional cigarettes under trademark Class 34 for tobacco products. It also registers IQOS electronic devices under Class 9 for hardware protection. This strategy allows the brand to secure complete protection across physical products and devices.
What Common Mistakes Occur During Class 34 Filing?
Many trademark applications under Class 34 face rejection because applicants ignore important filing rules. The following challenges delay registration, increase costs, and weaken brand protection in competitive markets.
Challenge 1: Filing Under the Wrong Trademark Class
Many applicants select the wrong class due to a poor understanding of classification rules. This mistake creates confusion during examination and results in trademark objections.
Solution: Businesses should study the Class 34 item list trademark before filing. Clear classification ensures accurate filing and faster approval.
Challenge 2: Using Vague or Incorrect Product Descriptions
Applicants often use vague or incorrect descriptions, such as “smoking products” instead of specifying “cigarettes, cigars, and tobacco substitutes.” This confuses examiners and delays the process.
Solution: Applicants should describe tobacco and smoking products precisely and clearly. Accurate descriptions reduce objections and strengthen trademark protection.
Challenge 3: Skipping the Trademark Search Process
Many businesses skip trademark searches and later face trademark infringement disputes. This oversight leads to opposition, rejection, or costly rebranding.
Solution: Businesses should conduct a detailed trademark search before filing. Early searches help avoid conflicts with existing trademarks.
Challenge 4: Ignoring Deadlines for Trademark Objections
Applicants sometimes miss deadlines while responding to trademark objections. This mistake results in application abandonment by the trademark registry.
Solution: Businesses should track deadlines carefully and respond within prescribed time limits. Timely responses keep applications active and moving forward.
Careful planning and compliance significantly reduce risks and protect brand value.
Frequently Asked Questions
Trademark Class 34 protects tobacco, smoking products, and related accessories. It covers cigarettes, cigars, electronic cigarettes, pipes, lighters, and other smoker-related goods. Filing under Class 34 gives businesses exclusive rights over their brand name, logo, and design. This protection prevents competitors from copying your identity and helps you maintain market credibility in India.




