
Trademark Class 23 covers yarns and threads used in textile and garment manufacturing. These include cotton, wool, silk, and linen yarn, sewing & embroidery thread, and synthetic or blended yarns. Textile mills, garment factories, embroidery units, handloom clusters, and export houses widely use these products. They serve both large-scale textile production and premium fashion, furnishing, and handicraft segments.
India’s textile industry is highly competitive and export-oriented. Trademark registration protects your yarn or thread brand from imitation. It establishes clear legal ownership and strengthens credibility with manufacturers, wholesalers, exporters, and international buyers.
Leading Indian and global textile companies register their yarn and thread brands under Trademark Class 23. Examples include Vardhman Yarns, RSWM (LNJ Bhilwara Group), Raymond (textile yarns), Bombay Dyeing (yarn divisions), and Coats (sewing and embroidery threads).
This guide explains how Trademark Class 23 helps protect and strengthen your textile brand in India.
What is Trademark Class 23 in India?
Trademark Class 23 defines a goods category under the Nice Classification system. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) administers this classification internationally. Class 23 applies to yarns and threads used for textile purposes, including cotton yarn, wool yarn, silk yarn, sewing thread, embroidery thread, and synthetic or blended yarns.
Businesses use this class for products supplied to textile manufacturing, garment production, embroidery units, and related industrial & commercial markets. In India, the Trade Marks Act, 1999, governs trademark registration under Class 23. The Indian Trademark Registry examines and enforces these applications based on the nature and intended use of the goods in textiles.
During examination, the Trademark Registry focuses on how the product functions within the textile value chain. It does not assess factors such as yarn thickness, fiber count, color variations, or packaging format. This method clearly separates yarns and threads from fabrics, garments, and other textile-related goods registered under different trademark classes.
Trademark registration under Class 23 is important because it:
- Protects yarn and thread brands from imitation and counterfeiting
- Builds confidence among textile manufacturers, distributors, exporters, and buyers
- Establishes legal ownership and strengthens enforcement rights
- Restricts unauthorized use and reduces brand misuse in the market
- Supports secure licensing, supply contracts, and interstate or export expansion
- Creates a strong, long-term brand asset in India’s textile industry
Note: Trademark registration under Class 23 does not replace other regulatory requirements. Businesses must still comply with applicable GST, factory, labor, and export regulations to operate lawfully in India.
Who Should Register Under Trademark Class 23?
You should register under Trademark Class 23 if your business deals with yarns or threads used in textile manufacturing. This class applies to a wide range of textile-focused businesses:
- Yarn manufacturers: Protect brand names used for cotton yarn, linen yarn, and synthetic or blended yarns. These products are supplied to the textile and garment industries.
- Sewing and embroidery thread producers: Register trademarks for sewing threads, embroidery threads, and specialty textile threads. Registration helps maintain a distinct brand identity in the market.
- Textile input suppliers: Safeguard brands used for yarns and threads supplied to textile mills, handloom units, and embroidery houses. These products also support export-oriented manufacturing units.
- Premium and specialty yarn brands: Secure trademarks for organic, eco-friendly, dyed, or luxury yarns. These products serve high-end fashion, furnishing, and technical textile segments.
- Importers and exporters of yarns and threads: Protect trademarks for international yarn and thread brands. This applies to goods imported into or exported from India.
- Private label yarn and thread producers: Register trademarks for yarns or threads they manufacture for textile houses and fashion brands. This also applies to export houses and institutional buyers.
- Textile brand licensors and marketers: Register trademarks used for licensing, franchising, and brand extensions. This helps maintain consistent brand control across markets.
- Suppliers and distributors of yarns and threads: Protect trademarks used in the marketing and distribution of yarns and threads. These products are supplied to textile mills, wholesalers, and exporters.
- Handloom and cottage industry yarn brands: Secure trademarks for traditional and artisanal yarn brands. These brands supply regional, handloom, and craft-based textile markets.
Several Indian and international textile companies protect their yarn and thread brands under Trademark Class 23. Examples include Welspun India, Indo Count Industries, Sutlej Textiles, Alok Industries, and Filatex India, which operate across cotton, blended, and synthetic yarn segments.
What are the Goods Covered Under Trademark Class 23?
Trademark Class 23 covers yarns and threads intended for textile use. These goods form the foundation for textile and garment manufacturing. Businesses supply these yarns and threads to textile mills, garment factories, embroidery units, and handloom clusters. They also serve export-oriented production units.
The table below outlines the main categories and examples of goods covered under Trademark Class 23 in India:
| Category | Examples of Goods Covered |
| Textile Yarns | Cotton yarn, wool yarn, silk yarn, linen yarn, jute yarn |
| Synthetic & Blended Yarns | Polyester yarn, nylon yarn, acrylic yarn, viscose yarn, blended yarns |
| Sewing Threads | Sewing threads used for garments, upholstery, footwear, and general textile applications |
| Embroidery Threads | Embroidery threads, decorative threads, metallic embroidery threads |
| Industrial & Technical Threads | High-strength threads for industrial stitching, upholstery, automotive textiles, and technical uses |
| Knitting & Crochet Yarns | Yarns used for knitting, crochet, and related textile production |
| Handloom & Artisanal Yarns | Hand-spun yarns, natural fiber yarns, and traditional regional yarn varieties |
| Dyed & Specialty Yarns | Dyed yarns, colored yarns, and specialty performance-based yarns |
| Elastic Threads | Elastic threads and stretch yarns used for textile and garment production |
| Eco-Friendly & Organic Yarns | Organic cotton yarn, recycled fiber yarns, and sustainable textile yarns |
| Imported Yarns & Threads | Imported cotton yarn, synthetic yarns, and international specialty thread brands |
| Export-Oriented Yarn Products | Yarns and threads manufactured for export and international textile markets |
| Private Label Yarns & Threads | Yarns and threads manufactured for textile houses, fashion brands, or retail chains under private labels |
Note: Industrial and technical threads qualify under Class 23 only when used for textile or stitching purposes. Non-textile industrial threads fall outside this class.
Which Products are Excluded from Trademark Class 23?
Some related products fall under other trademark classes and are not covered under Trademark Class 23. These include:
- Raw textile fibers: Raw cotton, silk, flax, hemp, and synthetic staple fibers are classified under Class 22. These fibers are not yet processed into yarns or threads.
- Textile fabrics: Woven, knitted, and nonwoven fabrics, bed linen, curtains, towels, and upholstery materials fall under Class 24. They are distinct from yarns and threads.
- Finished garments and apparel: Clothing, footwear, headwear, uniforms, and ready-made garments are included in Class 25.
- Industrial fibers not for textile use: Fiberglass, carbon fibers, insulation fibers, and other non-textile industrial fibers fall under Class 17 or Class 22, depending on their application.
- Textile machinery and equipment: Spinning machines, weaving looms, knitting machines, and sewing machines belong to Class 7.
- Needles, hooks, and sewing tools: Knitting needles, crochet hooks, and hand sewing tools are classified under Class 26.
- Chemical treatments and textile auxiliaries: Dyes, bleaching agents, textile finishing chemicals, and starches fall under Class 1 or Class 2.
- Non-textile threads: Threads used for industrial binding, packaging, medical sutures, or electrical purposes are outside Class 23.
- Handloom raw or semi-processed yarn: Hand-spun fibers not twisted or processed into yarns are also classified under Class 22.
Tip: Use RegisterKaro’s Trademark Class Finder to identify the correct class for your yarn or thread products. Proper classification avoids objections, reduces delays, and ensures smooth trademark registration with strong legal protection.
How to Register a Trademark Under Class 23 in India?
To register a trademark under Class 23 in India, follow a clear, step-by-step process. You may file as “proposed to be used” if your yarns or threads are not yet launched, or as “already in use” if they are currently supplied to the market.
Follow these steps for smooth Class 23 trademark registration in India:
Step 1. Conduct a Trademark Search
Check whether your brand name, logo, or yarn/thread product already exists under Class 23. This helps avoid conflicts, objections, or rejection later.
Use the official IP India trademark database or seek professional help for a detailed search.
Tip: Use RegisterKaro’s trademark availability check tool to quickly verify availability for cotton, wool, silk, linen, synthetic, and blended yarns.
Step 2. Select the Right Goods Description
- Clearly list all yarns and threads you want to protect, including sewing threads, embroidery threads, knitting yarns, industrial threads, and specialty yarns.
- Accurate descriptions reduce objections and strengthen legal protection.
Step 3. File the Trademark Application (Form TM-A)
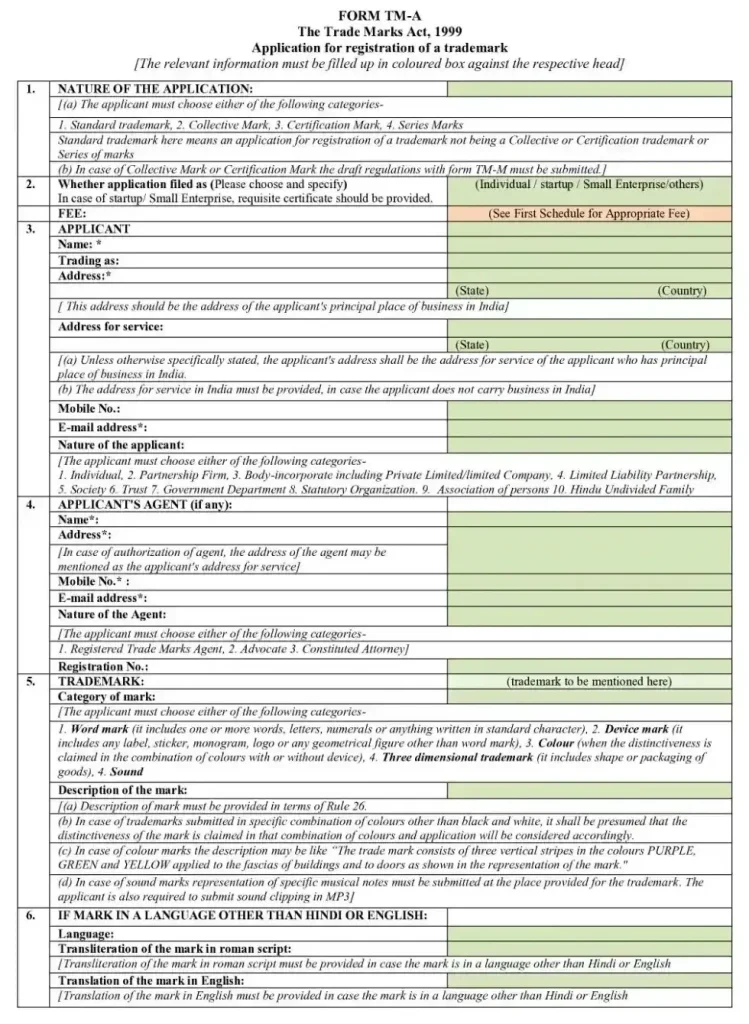
- Apply online through the IP India Trademark Portal or offline at the Trademark Registry.
- Include your brand name, logo (if any), detailed product descriptions, and applicant details.
Pay the applicable filing fee, usually ₹4,500 for individuals/startups and ₹9,000 for companies.
Step 4. Examination by the Trademark Office
- The Trademark Registrar examines your application for errors, similarities, or legal issues.
- If required, the Office issues an Examination Report requesting clarification or corrections.
Respond within the timeline to avoid delays.
Step 5. Publication in the Trademark Journal
- Once the Trademark Office accepts your application, it publishes your trademark in the Trademark Journal.
- This allows the public to file objections, usually within four months.
6. Registration and Issuance of Certificate
- If no trademark opposition is filed, or all objections are resolved, your mark is registered.
- You receive a Trademark Registration Certificate, granting exclusive rights under Class 23.
- Use the ® symbol to show your trademark is registered.
The process usually takes 12–18 months.
A trademark is valid for 10 years, and trademark renewal can be done indefinitely to ensure continuous protection for your yarn or thread brand.
Most businesses prefer expert guidance to avoid mistakes and delays. RegisterKaro helps you through every step, from trademark search to certificate issuance. Secure your Class 23 trademark in India today and protect your textile brand with confidence. Contact us today!
Trademark Classes Related to Class 23: Multi-Class Filings
Yarn and thread brands often offer products or services that span multiple trademark classes. Filing in related classes alongside Trademark Class 23 helps ensure complete protection across all connected categories.
The table below shows trademark classes that often overlap with Class 23:
| Related Class | Goods / Services Covered | Why It Relates to Class 23 |
| Class 24 | Woven, knitted, and nonwoven fabrics, curtains, towels | Fabrics made from yarns and threads fall under Class 24 instead of Class 23 |
| Class 25 | Clothing, headwear, uniforms, ready-made garments | Garments produced using yarns and threads belong to Class 25 |
| Class 26 | Sewing notions, crochet hooks, buttons, fasteners | Tools and accessories used with yarns and threads are classified under Class 26 |
| Class 35 | Wholesale, distribution, and retail services for yarns and threads | Services related to the sale, marketing, or distribution of yarns and threads fall under Class 35 |
| Class 7 | Spinning machines, weaving looms, and other textile machinery | Machinery used to produce or process yarns belongs to Class 7 |
| Class 1 & 2 (Optional) | Textile dyes, finishing chemicals, and textile auxiliaries | Chemical products used with yarns or threads are registered under Class 1 or 2 |
Filing trademarks in these related classes alongside Class 23 ensures your brand is fully protected across both products and services in the textile industry.
For example:
- Vardhman Textiles files its cotton and polyester yarns under Class 23 and its distribution and wholesale services under Class 35.
- Raymond Ltd. registers wool yarns under Class 23, suiting fabrics under Class 24, and clothing lines under Class 25.
This multi-class strategy safeguards your brand identity, prevents unauthorized use, and strengthens recognition across the textile supply chain.
Tip: Consider registering in all applicable classes if your brand produces specialty yarns, eco-friendly fibers, or textile chemicals. This ensures maximum legal protection and avoids gaps in trademark coverage.
Common Mistakes When Filing Under Class 23 and How to Avoid Them
Registering a Trademark Class 23 may seem easy, but errors can slow down approval or weaken protection. Some frequent pitfalls include:
- Wrong Classification: Make sure your products are correctly filed under Class 23. This class includes yarns and threads for textile use, such as cotton, wool, silk, linen, and blended fibers. Avoid misfiling under Class 24 (fabrics), Class 25 (apparel), Class 26 (sewing tools), or Class 7 (textile machines).
- Vague Product Descriptions: Broad terms like “thread” or “yarn” can trigger objections. Be specific. Describe products as “cotton embroidery thread,” “wool knitting yarn,” “polyester sewing thread,” or “industrial textile yarn.” Clear descriptions improve approval chances.
- Skipping Related Classes: Many companies offer products that extend beyond yarns and threads. Filing only under Class 23 may leave fabrics, garments, or sales services unprotected. Consider additional classes, such as Class 24 for fabrics, Class 25 for clothing, Class 26 for sewing accessories, and Class 35 for wholesale or retail operations.
- Weak or Generic Brand Names: Names like “Best Yarn” or “Quality Thread” are hard to defend legally. Choose unique or coined names such as “VardTex” or “SilkLine”. Distinctive names strengthen trademark rights.
- Not Checking Existing Trademarks: Conduct a search before applying. Look for similar brand names, logos, and labels in the textile industry. Overlooking this step can lead to rejections or legal conflicts.
- Ignoring Regulatory Standards: While trademarks protect your brand, some specialty or industrial yarns may require compliance with safety or manufacturing regulations. Ensure all standards are met before selling.
Avoiding these mistakes helps protect your textile brand over the long term. RegisterKaro assists throughout the Class 23 registration process. We ensure your filing is accurate, classification is correct, and the approval process is smooth. Fill the form to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions
Trademark Class 23 in India covers yarns and threads used for textile manufacturing, including sewing threads, embroidery threads, cotton yarn, silk yarn, wool yarn, and synthetic yarns. Registering under Class 23 legally protects brand names, logos, and labels used in the textile supply chain. It prevents imitation, establishes ownership, and strengthens credibility in India’s competitive textile and garment industry.


























