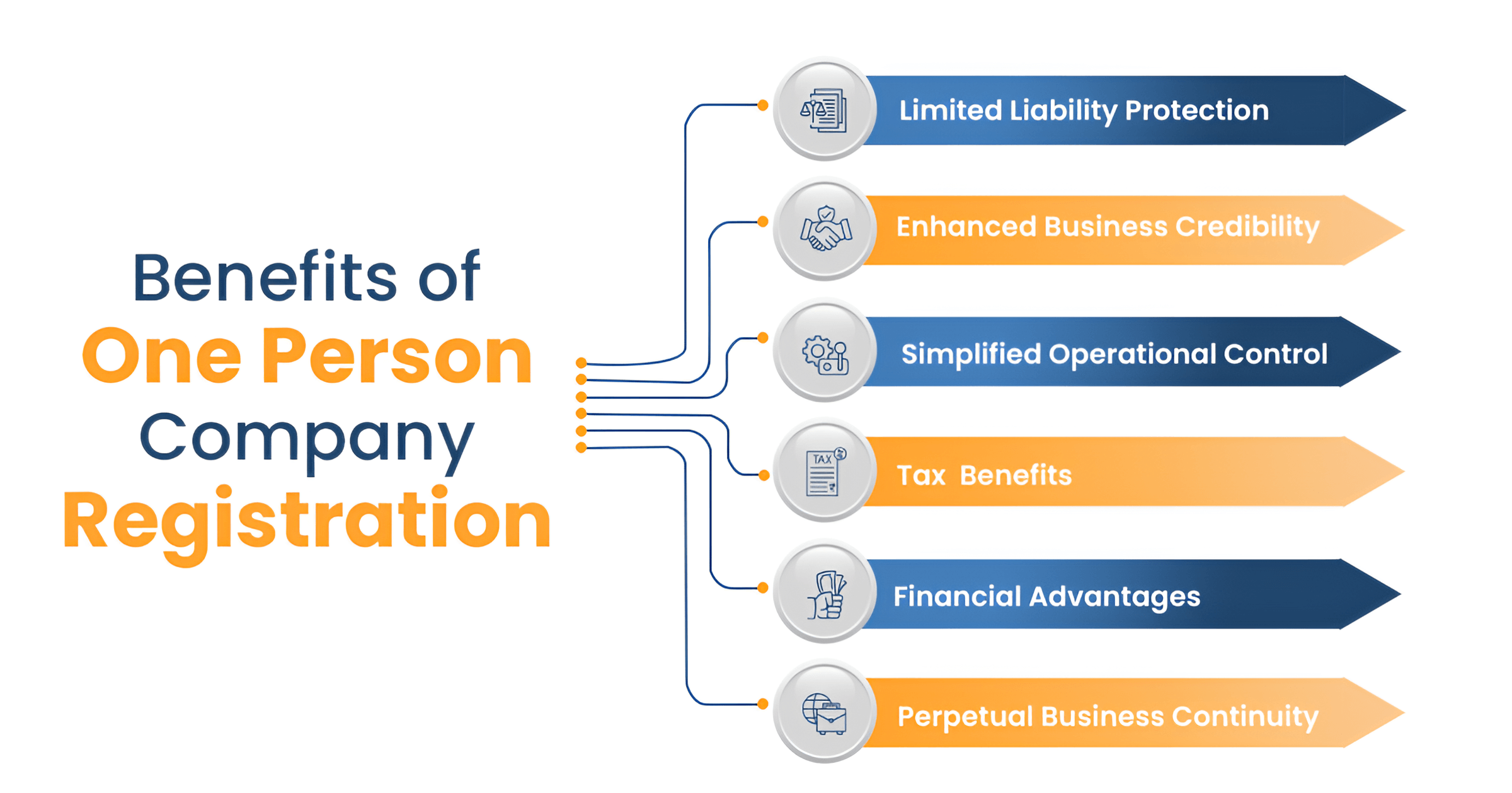
A One Person Company (OPC) is a business structure introduced under the Companies Act, 2013, that allows a single Indian citizen and resident to form a private limited company. It gives the sole owner full control to make decisions with limited liability, separate legal status, and perpetual succession. OPCs must appoint a nominee to take over in case the owner is incapacitated or dies.
The sole owner of the OPC acts as both shareholder and director, with a nominee appointed for succession. Initiated by a promoter, an OPC business model combines the simplicity of a sole proprietorship with limited liability.
With minimal compliance, no fixed capital requirement, and professional credibility, an OPC registration supports growth for new founders. OPC can also be converted into a private or public company if financial thresholds are exceeded.
Types of One Person Company in India
Planning to register a one-person company in India? Let's check out your options:
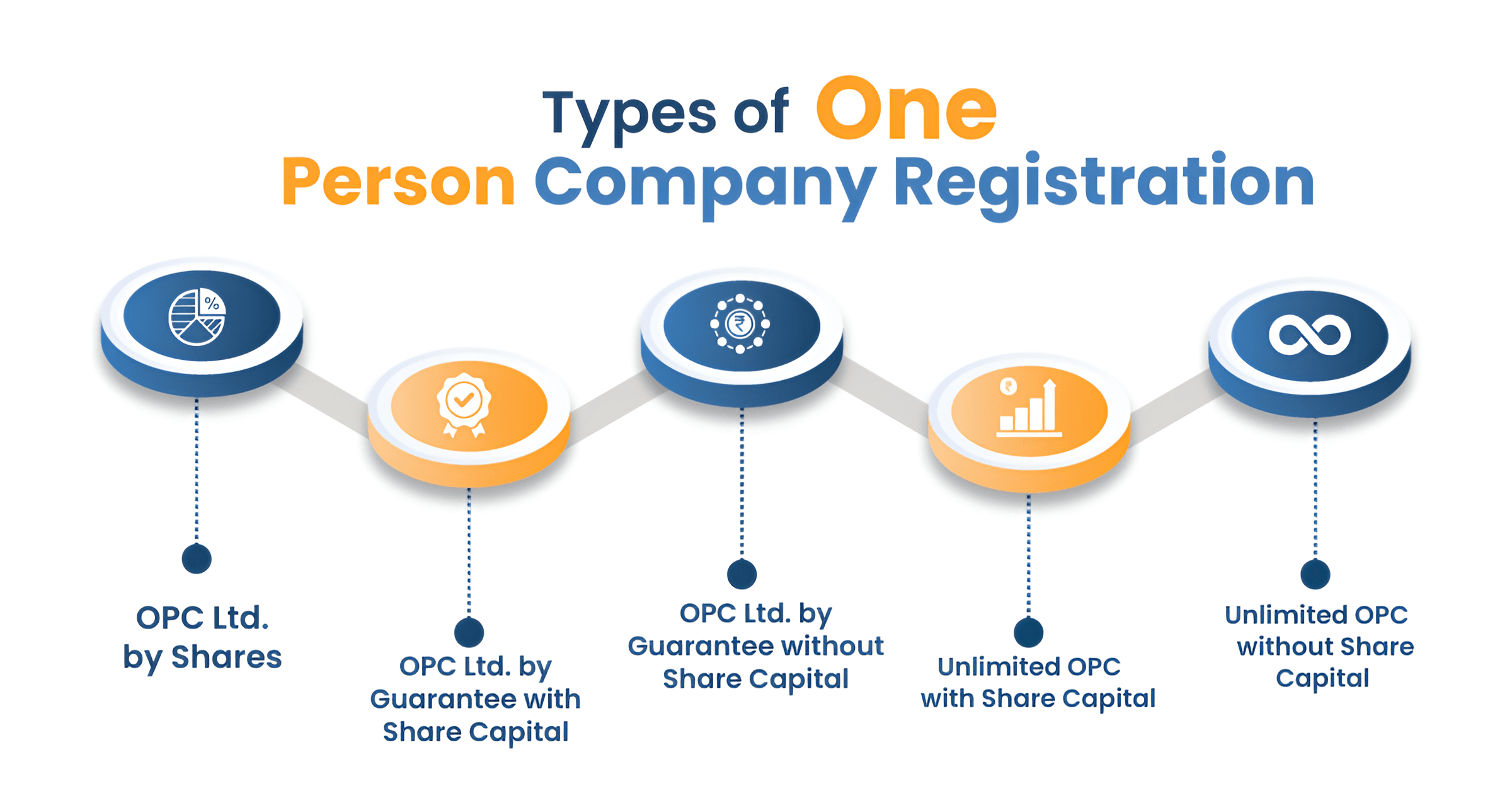
- OPC Limited by Shares: It falls under Section 2(22) & 2(68). Your liability stays limited to your unpaid share value. This gives you solid protection from business debts. This is the most popular option amongst entrepreneurs for OPC registration.
- OPC Limited by Guarantee with Share Capital: This type combines shares with a guarantee clause. Your liability includes both unpaid shares and the guaranteed amount. It offers a flexible capital structure.
- OPC Limited by Guarantee without Share Capital: This type, under Section 2(21), creates an entity without shares. Your liability is based only on your contribution guarantee if the company shuts down.
- Unlimited OPC with Share Capital: This type includes share capital but offers no liability protection. You remain personally responsible for all company debts. High-risk option, but with flexible capital handling.
- Unlimited OPC without Share Capital: This has neither share capital nor liability protection. You face unlimited personal responsibility. Very few choose this due to the high personal risk.